Page 12 - GTM-1-2
P. 12
Global Translational Medicine Effect of leptin on aortic dissection
results showed that there was a statistical difference in the
reduction of aortic dilatation compared with the control
group. The meta-analysis of all four studies (including
five animal experiments) showed that the increase in local
leptin content had a statistically significant effect on aortic
dilatation, with a combined RR of 0.11 (95% CI: 0.01 –
0.22; P = 0.0001; random effects model) and statistical
heterogeneity (P < 0.0001; I = 95.7%). The increase in local
2
leptin content promoted the dilation of mouse aorta. The
forest plot is shown in Figure 3.
3.5. Publication bias results
First, a funnel chart was used to conduct a qualitative
analysis of publication bias (sensitivity analysis based
on the difference in artery diameter) for the included
literature, showing that the distribution was asymmetric.
For further verification, Egger’s test was conducted, and
the results showed that there was no publication bias,
P = 0.988 (>0.05) (Figure 4 and Figure S1).
3.6. Sensitivity analysis
Due to the differences in the quality and sample size of the
studies, the heterogeneity among the studies was significant.
A sensitivity analysis was conducted to verify the reliability
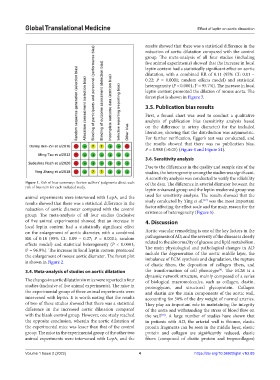
Figure 1. Risk of bias summary: Review authors’ judgments about each of the data. The difference in arterial diameter between the
risk of bias item for each included study.
leptin enhanced group and the leptin weakened group was
animal experiments were intervened with LepA, and the used for sensitivity analysis. The results showed that the
[17]
results showed that there was a statistical difference in the study conducted by Ying et al. was the most important
reduction of aortic diameter compared with the control factor affecting the effect scale and the main reason for the
existence of heterogeneity (Figure 5).
group. The meta-analysis of all four studies (inclusive
of five animal experiments) showed that an increase in 4. Discussion
local leptin content had a statistically significant effect
on the enlargement of aortic diameter, with a combined Aortic vascular remodeling is one of the key factors in the
RR of 0.18 (95% CI: 0.09 – 0.27; P = 0.0001; random pathogenesis of AD, and the severity of the disease is closely
effects model) and statistical heterogeneity (P < 0.0001; related to the abnormality of glucose and lipid metabolism.
I = 96.9%). The increase in local leptin content promoted The main physiological and pathological changes in AD
2
the enlargement of mouse aortic diameter. The forest plot include the degeneration of the aortic middle layer, the
imbalance of ECM synthesis and degradation, the rupture
is shown in Figure 2.
of elastic fibers, the deposition of collagen fibers, and
[9]
3.4. Meta-analysis of studies on aortic dilatation the transformation of cell phenotype . The ECM is a
dynamic network structure, mainly composed of a series
The changes in aortic dilatation in mice were reported in four of biological macromolecules, such as collagen, elastin,
studies (inclusive of five animal experiments). The mice in proteoglycan, and structural glycoprotein. Collagen
the experimental group of three animal experiments were and elastin are the main components of the aortic wall,
intervened with leptin. It is worth noting that the results accounting for 50% of the dry weight of normal arteries.
of two of these studies showed that there was a statistical They play an important role in maintaining the integrity
difference in the increased aortic dilatation compared of the aorta and withstanding the stress of blood flow on
with the blank control group. However, one study reached the wall . A large number of studies have shown that
[10]
the opposite conclusion, wherein the aortic dilatation of in patients with AD, the arterial wall is thinner, elastic
the experimental mice was lesser than that of the control protein fragments can be seen in the middle layer, elastic
group. The mice in the experimental group of the other two protein and collagen are significantly reduced, elastic
animal experiments were intervened with LepA, and the fibers (composed of elastic protein and tropocollagen)
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.85