Page 37 - GTM-1-2
P. 37
Global Translational Medicine Proteomic analysis of heart in metabolic cardiomyopathy
A B
C
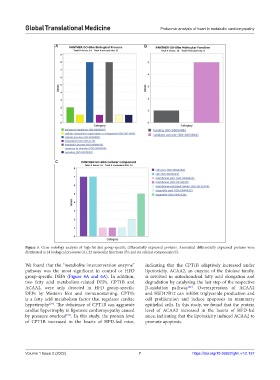
Figure 5. Gene ontology analysis of high-fat diet group-specific differentially expressed proteins. Annotated differentially expressed proteins were
distributed in 24 biological processes (A), 22 molecular functions (B), and six cellular components (C).
We found that the “metabolite interconversion enzyme” indicating that the CPT1B adaptively increased under
pathway was the most significant in control or HFD lipotoxicity. ACAA2, an enzyme of the thiolase family,
group-specific DEPs (Figure 4A and 6A). In addition, is involved in mitochondrial fatty acid elongation and
two fatty acid metabolism-related DEPs, CPT1B and degradation by catalyzing the last step of the respective
ACAA2, were only detected in HFD group-specific β-oxidation pathway . Overexpression of ACAA2
[26]
DEPs by Western blot and immunostaining. CPT1b and HSD17B12 can inhibit triglyceride production and
is a fatty acid metabolism factor that regulates cardiac cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in mammary
hypertrophy . The deficiency of CPT1B can aggravate epithelial cells. In this study, we found that the protein
[24]
cardiac hypertrophy in lipotoxic cardiomyopathy caused level of ACAA2 increased in the hearts of HFD-fed
by pressure overload . In this study, the protein level mice, indicating that the lipotoxicity induced ACAA2 to
[25]
of CPT1B increased in the hearts of HFD-fed mice, promote apoptosis.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.137