Page 16 - GTM-2-3
P. 16
Global Translational Medicine Hydrogen for acute lung injury
A B
Figure 10. (A) Trim and fill plot of wet-to-dry ratio; (B) sensitivity analysis of wet-to-dry ratio.
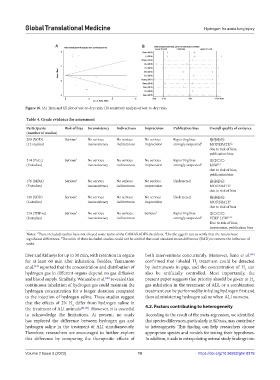
Table 4. Grade evidence for assessment
Participants Risk of bias Inconsistency Indirectness Imprecision Publication bias Overall quality of evidence
(number of studies)
200 (W/D) Serious 1 No serious No serious No serious Reporting bias ⊕⊕⊕⊝
(12 studies) inconsistency indirectness imprecision strongly suspected 2 MODERATE 1,2,
due to risk of bias,
publication bias
214 (PaO ) Serious 1 No serious No serious No serious Reporting bias ⊕⊕⊝⊝
2
(9 studies) inconsistency indirectness imprecision strongly suspected 2 LOW 1,2
due to risk of bias,
publication bias
176 (MDA) Serious 1 No serious No serious No serious Undetected ⊕⊕⊕⊝
(9 studies) inconsistency indirectness imprecision MODERATE 1
due to risk of bias
128 (SOD) Serious 1 No serious No serious No serious Undetected ⊕⊕⊕⊝
(6 studies) inconsistency indirectness imprecision MODERATE 1
due to risk of bias
170 (TNF-α) Serious 1 No serious No serious Serious 3 Reporting bias ⊕⊝⊝⊝
(8 studies) inconsistency indirectness strongly suspected 2 VERY LOW 1,2,3
Due to risk of bias,
imprecision, publication bias
Notes: These included studies have not obeyed some items of the CAMARADES checklists. Use the egger’s test to verify that the results have
2
1
significant differences. The units of these included studies could not be unified that used standard mean difference (SMD) to remove the influence of
3
units.
[46]
liver and kidneys for up to 30 min, with retention in organs both interventions concurrently. Moreover, Sano et al.
for at least 60 min after inhalation. Besides, Yamamoto confirmed that inhaled H treatment could be detected
2
et al. reported that the concentration and distribution of by instruments in pigs, and the concentration of H can
[44]
2
hydrogen gas in different organs depend on gas diffusion also be artificially controlled. Most importantly, the
and blood supply. Similarly, Watanabe et al. revealed that present paper suggests that priority should be given to H
[45]
2
continuous inhalation of hydrogen gas could maintain the gas inhalation in the treatment of ALI, or a combination
hydrogen concentration for a longer duration compared treatment can be performed by inhaling hydrogen first and
to the injection of hydrogen saline. These studies suggest then administering hydrogen saline when ALI worsens.
that the effects of 2% H differ from hydrogen saline in
2
the treatment of ALI animals [43-45] . However, it is essential 4.2. Factors contributing to heterogeneity
to acknowledge the limitations. At present, no study According to the result of the meta-regression, we identified
has explored the difference between hydrogen gas and that species differences, particularly in SD rats, may contribute
hydrogen saline in the treatment of ALI simultaneously. to heterogeneity. This finding can help researchers choose
Therefore, researchers are encouraged to further explore appropriate species and models for testing their hypotheses.
this difference by comparing the therapeutic effects of In addition, it aids in extrapolating animal study findings into
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.0379