Page 42 - GTM-2-3
P. 42
Global Translational Medicine Deep learning by NMR-biochemical
A B
Figure 8. (A) Image-based extracted phenotypes on digital mammograms of breast parenchyma show the risk of breast cancer reoccurrence . (B) Distinct
[18]
cancer and non-cancer features show the likelihood of malignancy by deep learning. https://radiologykey.com/13-future-applications-radiomics-and-
deep-learning-on-breast-mri/.
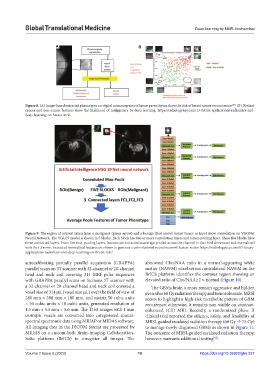
Figure 9. The region of interest taken from a malignant (green arrow) and a benign (Red arrow) breast tumor as input show convolution on VGGNet
Neural Network. The VGG19 model is shown in 5 blocks. Each block has two or more convolution layers and a max‑pooling layer. These five blocks have
three connected layers. From five max-pooling layers, features are extracted as average-pooled across the channel in the third dimension and normalized
with the L2 norm. Extracted normalized features are shown to generate a convolutional neural network feature vector. https://radiologykey.com/13-future-
applications-radiomics-and-deep-learning-on-breast-mri/.
autocalibrating partially parallel acquisition (GRAPPA) abnormal Cho/NAA ratio in a normal-appearing white
parallel scans on 3T scanner with 32-channel or 20-channel matter (NAWM) voxel versus contralateral NAWM on the
head and neck coil covering 314 MRI pulse sequences BrICS platform identifies the contour region showing an
with GRAPPA parallel scans on Siemens 3T scanner with elevated ratio of Cho/NAA≥2 × normal (Figure 10).
a 32-channel or 20-channel head and neck coil covered a The GBMs brain tumors remain aggressive and hidden
voxel size of 314 μL (voxel size μL) over the field of view of even after 60 Gy radiation therapy and temozolomide. MRSI
280 mm × 280 mm × 180 mm, and matrix 50 cubic units seems to highlight a high‑risk metabolite pattern of GBM
× 50 cubic units × 18 cubic units, generated resolution of recurrence; otherwise, it remains non‑visible on contrast‑
4.5 mm × 4.5 mm × 5.6 mm. The T1wt images with 1 mm enhanced (CE) MRI. Recently, a randomized phase II
isotropic voxels are converted into coregistered spatial- clinical trial reported the efficacy, safety, and feasibility of
spectral spectromic data using MRIAP or MIDAS software. MRSI‑guided escalated radiation therapy (60 Gy 75 Gy)
All imaging data in the DICOM format are processed by to manage newly diagnosed GBMs as shown in Figure 11.
MIDAS on a custom‑built Brain‑Imaging‑Collaboration‑ The outcome of MRSI-guided escalated radiation therapy,
Suite platform (BrICS) to coregister all images. The however, warrants additional testing .
[62]
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.337