Page 41 - GTM-2-3
P. 41
Global Translational Medicine Deep learning by NMR-biochemical
[HER2], estrogen receptor [ER], and progesterone receptor of breast cancer gene expression categorize tumors into
[PR]) further classifies tumors into subtypes. The profiles molecular subtypes of basal-like, normal-like luminal A,
luminal B, and HER2‑enriched tumors. Different breast
cancer subtypes have different MRI radiomic features
serving as prognostic indicators called PR+ versus PR‑,
ER+ versus ER‑, HER2+ versus HER2‑, and triple‑negative
tumors or cancers. All these respond differently to different
therapies and are used in DL.
In short, DL information from computer-extracted MRI-
visible soft-tissue tumor features with metabolite phenotypes
distinguish breast cancer subtypes by quantitative signatures
to predict prognosis for precision medicine.
3.2. Classification of brain GBM tumors
In GBM tumor cells, cell membrane show increased Cho‑
containing phospholipids concentration in proliferating
cells, while N-acetylaspartate (NAA) compounds in
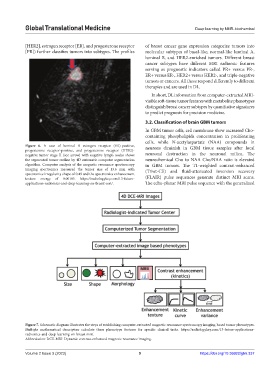
Figure 6. A case of luminal A estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, neurons diminish in GBM tissue samples after local
progesterone receptor-positive, and progesterone receptor (HER2)-
negative tumor stage II (see arrow) with negative lymph nodes shows neuronal destruction in the neuronal milieu. The
the segmented tumor outline by 4D automatic computer segmentation neurochemical Cho to NAA Cho/NAA ratio is elevated
algorithm. Computer analysis of the magnetic resonance spectroscopy in GBM tumors. The T1‑weighted contrast‑enhanced
imaging spectromics measured the tumor size of 13.6 mm with (T1wt-CE) and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
spectromics irregularity shape of 0.49 and the spectromics enhancement
texture energy of 0.00185. https://radiologykey.com/13-future- (FLAIR) pulse sequences generate distinct MRI scans.
applications-radiomics-and-deep-learning-on-breast-mri/. The echo-planar MRI pulse sequence with the generalized
Figure 7. Schematic diagram illustrates the steps of establishing computer-extracted magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging-based tumor phenotypes.
Multiple mathematical descriptors calculate these phenotype features for specific clinical tasks. https://radiologykey.com/13-future-applications-
radiomics-and-deep-learning-on-breast-mri/.
Abbreviation: DCE-MRI: Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.337