Page 101 - GTM-2-4
P. 101
Global Translational Medicine ECM receptor pathway in endotheliocytes after MI
A B
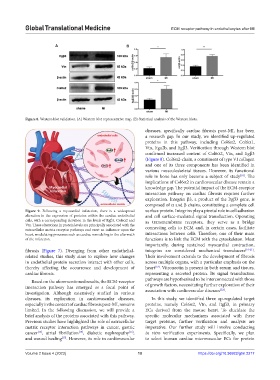
Figure 8. Western blot validation. (A) Western blot representative map. (B) Statistical analysis of the Western blots.
diseases, specifically cardiac fibrosis post-MI, has been
a research gap. In our study, we identified up-regulated
proteins in this pathway, including Col6α2, Col6α1,
Vtn, Itga2b, and Itgβ3. Verification through Western blot
confirmed increased content of Col6α2, Vtn, and Itgβ3
(Figure 8). Col6α2-chain, a constituent of type VI collagen
and one of its three components has been identified in
various musculoskeletal tissues. However, its functional
role in bone has only become a subject of study . The
[18]
implications of Col6α2 in cardiovascular disease remain a
knowledge gap. The potential impact of the ECM-receptor
interaction pathway on cardiac fibrosis requires further
exploration. Integrin β3, a product of the Itgβ3 gene, is
composed of α and β chains, constituting a complete cell
Figure 9. Following a myocardial infarction, there is a widespread surface protein. Integrins play a pivotal role in cell adhesion
alteration in the expression of proteins within the cardiac endothelial and cell surface-mediated signal transduction. Operating
cells, with a corresponding elevation in the levels of Itgβ3, Col6α2 and as transmembrane receptors, they serve as a bridge
Vtn. These alterations in protein levels are principally associated with the connecting cells to ECM and, in certain cases, facilitate
extracellular matrix receptor pathways and exert an influence upon the
heart, modulating processes such as cardiac remodeling in the aftermath interactions between cells. Therefore, one of their main
of the infarction. functions is to link the ECM with the cytoskeleton. Most
importantly, during sustained myocardial contraction,
fibrosis (Figure 7). Diverging from other endothelial- integrins are considered mechanical transducers [19-21] .
related studies, this study aims to explore how changes Their involvement extends to the development of fibrosis
in endothelial protein secretion interact with other cells, across multiple organs, with a particular emphasis on the
thereby affecting the occurrence and development of heart . Vitronectin is present in both serum and tissues,
[22]
cardiac fibrosis. representing a secreted protein. Its signal transduction
pathways are hypothesized to be interconnected with those
Based on the aforementioned results, the ECM-receptor
interaction pathway has emerged as a focal point of of growth factors, necessitating further exploration of their
[23]
investigation. Although extensively studied in various association with cardiovascular diseases .
diseases, its exploration in cardiovascular diseases, In this study, we identified three up-regulated target
especially in the context of cardiac fibrosis post-MI, remains proteins, namely Col6α2, Vtn, and Itgβ3, in primary
limited. In the following discussion, we will provide a ECs derived from the mouse heart. To elucidate the
brief analysis of the proteins associated with this pathway. specific molecular mechanisms associated with these
Previous studies have highlighted the role of extracellular target proteins, further verification and analysis are
matrix receptor interaction pathways in cancer, gastric imperative. Our further study will involve conducting
cancer , atrial fibrillation , diabetic nephropathy , in vitro verification experiments. Specifically, we plan
[14]
[15]
[16]
and wound healing . However, its role in cardiovascular to select human cardiac microvascular ECs for protein
[17]
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.2217