Page 103 - GTM-3-3
P. 103
Global Translational Medicine Rheumatoid nodule versus fibrocaseous tubercle
A D A B
C D
B E
E F
C F
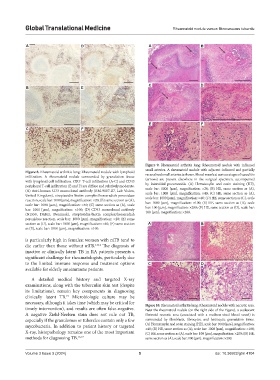
Figure 9. Rheumatoid arthritis lung: Rheumatoid nodule with inflamed
small arteries. A rheumatoid nodule with adjacent inflamed and partially
Figure 8. Rheumatoid arthritis lung: Rheumatoid nodule with lymphoid recanalized small arteries is shown. Blood vessels at various stages of vasculitis
infiltration. A rheumatoid nodule surrounded by granulation tissue (arrows) are present elsewhere in the surgical specimen, accompanied
with lymphoid cell infiltration. CD3 T-cell infiltration (A-C) and CD43 by interstitial pneumonitis. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin staining (HE),
+
peripheral T-cell infiltration (E and F) are diffuse and relatively moderate. scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×20; (B) HE, same section as (A),
(A) Anti-human CD3 monoclonal antibody (RM-9107-R7, Lab Vision, scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×40; (C) HE, same section as (A),
United Kingdom), streptavidin-biotin complex/horseradish peroxidase scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×40; (D) HE, same section as (C), scale
reaction, scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×20; (B) same section as (A), bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×100; (E) HE, same section as (D), scale
scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×40; (C) same section as (A), scale bar: 100 [µm], magnification: ×200; (F) HE, same section as (D), scale bar:
bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×100; (D) CD43 monoclonal antibody 100 [µm], magnification: ×200.
(N1559, DAKO, Denmark), streptavidin-biotin complex/horseradish
peroxidase reaction, scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×20; (E) same
section as (D), scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×40; (F) same section A B
as (E), scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×100.
is particularly high in females; women with mTB tend to
die earlier than those without mTB. 13,14 The diagnosis of
inactive or clinically latent TB in RA patients presents a
significant challenge for rheumatologists, particularly due
to the limited immune response and treatment options C D
available for elderly autoimmune patients.
A detailed medical history and targeted X-ray
examinations, along with the tuberculin skin test (despite
its limitations), remain key components in diagnosing
clinically latent TB. Microbiologic culture may be
15
necessary, although it takes time (which may be critical for Figure 10. Rheumatoid arthritis lung: Rheumatoid nodule with necrotic area.
timely intervention), and results are often false-negative. Near the rheumatoid nodule (on the right side of the Figure), a coalescent
A negative Ziehl-Neelsen stain does not rule out TB, fibrinoid necrotic area (associated with a medium-sized blood vessel) is
especially if the granulomas or tubercles contain only a few surrounded by fibroblasts, fibrocytes, and histiocytic granulation tissue.
mycobacteria. In addition to patient history or targeted (A) Hematoxylin and eosin staining (HE), scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification:
×40; (B) HE, same section as (A), scale bar: 1000 [µm], magnification: ×100;
X-ray, histopathology remains one of the most important (C) HE, same section as (A), scale bar: 100 [µm], magnification: ×200; (D) HE,
methods for diagnosing TB. 16,17 same section as (A), scale bar: 100 [µm], magnification: ×200.
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gtm.4104