Page 79 - GTM-3-3
P. 79
Global Translational Medicine Graphene oxide in cancer drug delivery applications
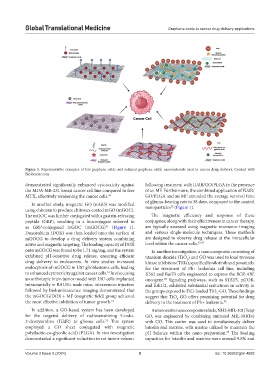
Figure 1. Representative examples of few graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide nanomaterials used in cancer drug delivery. Created with
BioRender.com
demonstrated significantly enhanced cytotoxicity against following treatment with IUdR/GO/PLGA in the presence
the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line compared to free of an MF. Furthermore, the combined application of IUdR/
MTX, effectively weakening the cancer cells. 50 GO/PLGA and an MF extended the average survival time
In another study, magnetic GO (mGO) was modified of glioma-bearing rats to 38 days, compared to the control
52
using chitosan to produce chitosan-coated mGO (mGOC). nanoparticles (Figure 1).
The mGOC was further conjugated with a gastrin-releasing The magnetic efficiency and response of these
peptide (GRP), resulting in a bioconjugate referred to conjugates, along with their effectiveness in cancer therapy,
as GRP-conjugated mGOC (mGOCG) (Figure 1). are typically assessed using magnetic resonance imaging
51
Doxorubicin (DOX) was then loaded onto the surface of and various single-molecule techniques. These methods
mGOCG to develop a drug delivery system combining are designed to observe drug release at the intracellular
active and magnetic targeting. The loading capacity of DOX level within the cancer cells. 53-57
onto mGOCG was found to be 1.71 mg/mg, and the system In another investigation, a nanocomposite consisting of
exhibited pH-sensitive drug release, ensuring efficient titanium dioxide (TiO ) and GO was used to load tyrosine
2
drug delivery to endosomes. In vitro studies increased kinase inhibitors (TKIs), specifically nilotinib and ponatinib,
endocytosis of mGOCG in U87 glioblastoma cells, leading for the treatment of Ph+ leukemia cell line, including
to enhanced cytotoxicity against cancer cells. In vivo, using K562 and Ba/F3 cells engineered to express the BCR-ABL
51
an orthotopic brain tumor model with U87 cells implanted oncogene. Signaling pathways, such as STAT5, mTOR,
58
intracranially in BALB/c nude mice, intravenous injection and Erk1/2, exhibited substantial reductions in activity in
followed by bioluminescence imaging demonstrated that the groups exposed to TKI-loaded TiO -GO. These findings
2
the mGOCG/DOX + MF (magnetic field) group achieved suggest that TiO -GO offers promising potential for drug
2
the most effective inhibition of tumor growth. 51 delivery in the treatment of Ph+ leukemia. 58
In addition, a GO-based system has been developed An innovative nanocomposite vehicle, NH2-MIL-101(Fe)@
for the targeted delivery of radiosensitizing 5-iodo- GO, was engineered by combining aminated MIL-101(Fe)
2-deoxyuridine (IUdR) to glioma cells. This system with GO. This carrier was used to simultaneously deliver
52
employed a GO sheet conjugated with magnetic luteolin and matrine, with marine utilized to maintain the
poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA). In vivo investigation pH balance within the nano-preparation. The loading
59
demonstrated a significant reduction in rat tumor volume capacities for luteolin and matrine were around 9.8% and
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gtm.4602