Page 89 - GTM-3-3
P. 89
Global Translational Medicine rh-PDGF for peri-intrabony defects
A B C
D E F
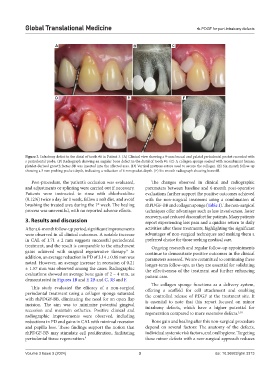
Figure 3. Infrabony defect in the distal of tooth #6 in Patient 3. (A) Clinical view showing a 9-mm buccal and palatal periodontal pocket recorded with
a periodontal probe. (B) Radiograph showing an angular bone defect in the distal of tooth #6. (C) A collagen sponge soaked with recombinant human
platelet-derived growth factor-BB was inserted into the affected area. (D) Vertical mattress suture used to secure the collagen. (E) Six-month follow-up
showing a 3 mm probing pocket depth, indicating a reduction of 6 mm pocket depth. (F) Six-month radiograph showing bone fill.
Post-procedure, the patient’s occlusion was evaluated, The changes observed in clinical and radiographic
and adjustments or splinting were carried out if necessary. parameters between baseline and 6-month post-operative
Patients were instructed to rinse with chlorhexidine evaluations further support the positive outcomes achieved
(0.12%) twice a day for 1 week, follow a soft diet, and avoid with the non-surgical treatment using a combination of
st
brushing the treated area during the 1 week. The healing rhPDGF-BB and collagen sponge (Table 1). The non-surgical
process was uneventful, with no reported adverse effects. techniques offer advantages such as less invasiveness, faster
recovery, and reduced discomfort for patients. Many patients
3. Results and discussion report experiencing less pain and a quicker return to daily
After a 6-month follow-up period, significant improvements activities after these treatments, highlighting the significant
were observed in all clinical outcomes. A notable increase advantages of non-surgical techniques and making them a
in CAL of 1.71 ± 2 mm suggests successful periodontal preferred choice for those seeking medical care.
treatment, and the result is comparable to the attachment Ongoing research and regular follow-up appointments
gains achieved with surgical regenerative therapy. In continue to demonstrate positive outcomes in the clinical
9
addition, an average reduction in PD of 3.14 ± 0.86 mm was parameters assessed. We are committed to continuing these
noted. However, an average increase in recession of 0.21 longer-term follow-ups, as they are essential for validating
± 1.57 mm was observed among the cases. Radiographic the effectiveness of the treatment and further enhancing
evaluations showed an average bone gain of 2 – 4 mm, as patient care.
demonstrated in Figures 1B and F, 2B and C, 3B and F.
The collagen sponge functions as a delivery system,
This study evaluated the efficacy of a non-surgical offering a scaffold for cell attachment and enabling
periodontal treatment using a collagen sponge saturated the controlled release of PDGF at the treatment site. It
with rhPDGF-BB, eliminating the need for an open flap is essential to note that this report focused on minor
incision. The aim was to minimize potential gingival intrabony defects, which have a higher potential for
recession and maintain esthetics. Positive clinical and regeneration compared to more extensive defects. 1,10
radiographic improvements were observed, including
reductions in PD and gains in CAL with minimal recession Bone gain and healing after this non-surgical procedure
and papilla loss. These findings support the notion that depend on several factors: The anatomy of the defects,
rhPDGF-BB may stimulate cell proliferation, facilitating individual systemic risk factors, and oral hygiene. Targeting
periodontal tissue regeneration. 9 these minor defects with a non-surgical approach reduces
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/gtm.3313