Page 48 - GTM-4-1
P. 48
Global Translational Medicine Connective tissue harvest techniques
A B C
D E
F G
H I
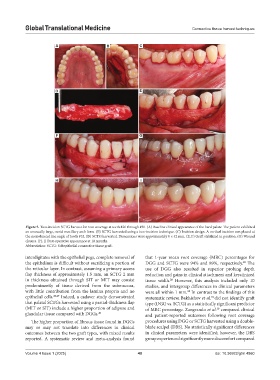
Figure 5. Two-incision SCTG harvest for root coverage at teeth #26 through #30. (A) Baseline clinical appearance of the hard palate. The patient exhibited
an unusually large, ovoid maxillary arch form. (B) SCTG harvested using a two-incision technique. (C) Incision design. A vertical incision was placed at
the mesiobuccal line angle of tooth #32. (D) SCTG harvested. Dimensions were approximately 8 × 42 mm. (E, F) Graft stabilized in position. (G) Wound
closure. (H, I) Post-operative appearance at 10 months.
Abbreviation: SCTG: Subepithelial connective tissue graft.
interdigitates with the epithelial pegs, complete removal of that 1-year mean root coverage (MRC) percentages for
the epithelium is difficult without sacrificing a portion of DGG and SCTG were 94% and 89%, respectively. The
28
the reticular layer. In contrast, assuming a primary access use of DGG also resulted in superior probing depth
flap thickness of approximately 1.5 mm, an SCTG 2 mm reduction and gains in clinical attachment and keratinized
in thickness obtained through SIT or MIT may consist tissue width. However, this analysis included only 10
28
predominantly of tissue derived from the submucosa, studies, and intergroup differences in clinical parameters
with little contribution from the lamina propria and no were all within 1 mm. In contrast to the findings of this
28
epithelial cells. 20,27 Indeed, a cadaver study demonstrated systematic review, Bakhishov et al. did not identify graft
29
that palatal SCTGs harvested using a partial-thickness flap type (DGG vs. SCTG) as a statistically significant predictor
(MIT or SIT) include a higher proportion of adipose and of MRC percentage. Zangrando et al. compared clinical
30
glandular tissue compared with DGGs. 20 and patient-reported outcomes following root coverage
The higher proportion of fibrous tissue found in DGGs procedures using DGG or SCTG harvested using a double-
may or may not translate into differences in clinical blade scalpel (DBS). No statistically significant differences
outcomes between the two graft types, with mixed results in clinical parameters were identified; however, the DBS
reported. A systematic review and meta-analysis found group experienced significantly more discomfort compared
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 40 doi: 10.36922/gtm.4860