Page 80 - GTM-4-1
P. 80
Global Translational Medicine Gelatin-based cell carriers for tooth-germ organoids
analyzed using the NIH ImageJ software. The RGB_ 3.1.1. Methacrylate gelatin microspheres
Measure.java plugin java file was used to measure the red Methacrylate gelatin microspheres were produced using
channel intensity of each sample. Data were then analyzed a water-in-oil emulsion method, followed by ammonium
using GraphPad Prism version 10.3.1 (United States). persulfate-initiated thermal crosslinking. This process
7
2.13. Statistical analysis involves multiple high-temperature steps (e.g., 100°C)
and requires the use of surfactants, nitrogen purging, and
For each experiment, biological repeats (n ≥ 3) were used, extensive washing (Figure 1A). It typically takes about
and data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. 2 days to obtain a clean batch ready for lyophilization.
One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons The labor-intensive, multi-step nature of this method
test was performed to determine statistical significance, contributes to significant batch-to-batch variability,
using GraphPad Prism version 10.3.1. Differences were presenting challenges for scaling up the process. The
considered significant at a P < 0.05. hydrated GelMA MS, which was measured to range from
50 to 250 µm with an average size of 134.75 ± 69.2 µm, was
3. Results and discussion used in this study (Figure 2A and E). This wide size range
3.1. Fabrication and characterization of gelatin- further underscores the challenges in producing large,
based cell carriers uniform batches of GelMA MS, which could hinder the
scalability required for larger studies. The characterization
To explore additional cell carrier options for culturing of these GelMA MS has been reported in our previous
hDPSCs, four configurations of gelatin-based HG materials study. Once lyophilized, GelMA MS remain shelf-stable
7
were prepared. when stored at 4°C, allowing for off-the-shelf use.
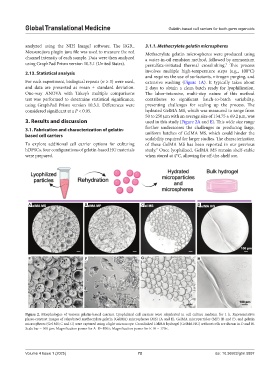
A B C D
E F G H
Figure 2. Morphologies of various gelatin-based carriers. Lyophilized cell carriers were rehydrated in cell culture medium for 1 h. Representative
phase-contrast images of rehydrated methacrylate gelatin (GelMA) microspheres (MS) (A and E), GelMA microparticles (MP) (B and F), and gelatin
microspheres (Gel MS; C and G) were captured using a light microscope. Crosslinked GelMA hydrogel (GelMA HG) without cells are shown in D and H.
Scale bar = 100 µm; Magnification power for A–D=100×; Magnification power for E–H = 170×.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 72 doi: 10.36922/gtm.5897