Page 94 - GTM-4-1
P. 94
Global Translational Medicine Brain morphology in obesity
A B A B
C D C D
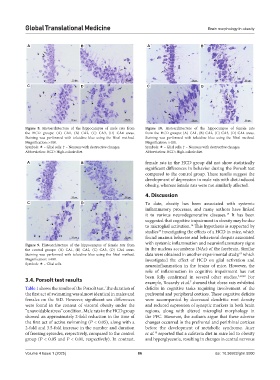
Figure 8. Histoarchitecture of the hippocampus of male rats from Figure 10. Histoarchitecture of the hippocampus of female rats
the HCD groups: (A) CA1, (B) CA2, (C) CA3, (D) CA4 areas. from the HCD groups: (A) CA1, (B) CA2, (C) CA3, (D) CA4 areas.
Staining was performed with toluidine blue using the Nissl method. Staining was performed with toluidine blue using the Nissl method.
Magnification: ×400. Magnification: ×400.
Symbols: – Glial cells. ↑ – Neurons with destructive changes. Symbols: – Glial cells. ↑ – Neurons with destructive changes.
Abbreviation: HCD: High-calorie diet. Abbreviation: HCD: High-calorie diet.
A B female rats in the HCD group did not show statistically
significant differences in behavior during the Porsolt test
compared to the control group. These results suggest the
development of depression in male rats with diet-induced
obesity, whereas female rats were not similarly affected.
4. Discussion
C D To date, obesity has been associated with systemic
inflammatory processes, and many authors have linked
it to various neurodegenerative diseases. It has been
15
suggested that cognitive impairment in obesity may be due
to microglial activation. This hypothesis is supported by
16
studies investigating the effects of a HCD in mice, which
17
found anxious behavior and behavioral despair associated
Figure 9. Histoarchitecture of the hippocampus of female rats from with systemic inflammation and neuroinflammatory signs
the control groups: (A) CA1, (B) CA2, (C) CA3, (D) CA4 areas. in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) of the forebrain. Similar
Staining was performed with toluidine blue using the Nissl method. data were obtained in another experimental study, which
18
Magnification: ×400. investigated the effect of HCD on glial activation and
Symbols: – Glial cells. neuroinflammation in the brains of mice. However, the
role of inflammation in cognitive impairment has not
3.4. Porsolt test results been fully confirmed in several other studies. 7,19,20 For
example, Bocarsly et al. showed that obese rats exhibited
7
Table 1 shows the results of the Porsolt test. The duration of deficits in cognitive tasks requiring involvement of the
the first act of swimming was almost identical in males and prefrontal and peripheral cortices. These cognitive deficits
females on the StD. However, significant sex differences were accompanied by decreased dendritic root density
were found in the context of visceral obesity under the and reduced expression of synaptic markers in both brain
“unavoidable stress” condition. Male rats in the HCD group regions, along with altered microglial morphology in
showed an approximately 2-fold reduction in the time of the PFC. However, the authors argue that these adverse
the first act of active swimming (P < 0.05), along with a changes occurred in the prefrontal and perirhinal cortices
2-fold and 3.5-fold increase in the number and duration before the development of metabolic syndrome. Auer
of freezing episodes, respectively, compared to the control et al. reported that a cafeteria diet in mice led to obesity
19
group (P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively). In contrast, and hyperglycemia, resulting in changes in central nervous
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 86 doi: 10.36922/gtm.5000