Page 64 - GTM-4-3
P. 64
Global Translational Medicine Recent community-based CVD interventions
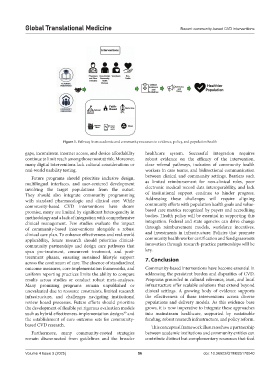
Figure 1. Pathway from academic and community resources to evidence, policy, and population health
gaps, inconsistent internet access, and device affordability healthcare system. Successful integration requires
continue to limit reach among those most at risk. Moreover, robust evidence on the efficacy of the intervention,
many digital interventions lack cultural considerations or clear referral pathways, inclusion of community health
real-world usability testing. workers in care teams, and bidirectional communication
Future programs should prioritize inclusive design, between clinical and community settings. Barriers such
multilingual interfaces, and user-centered development as limited reimbursement for non-clinical roles, poor
involving the target populations from the outset. electronic medical record data interoperability, and lack
They should also integrate community programming of institutional support continue to hinder progress.
with standard pharmacologic and clinical care. While Addressing these challenges will require aligning
community-based CVD interventions have shown community efforts with population health goals and value-
promise, many are limited by significant heterogeneity in based care metrics recognized by payers and accrediting
methodology and a lack of integration with comprehensive bodies. Health policy will be essential in supporting this
clinical management. Few studies evaluate the impact integration. Federal and state agencies can drive change
of community-based interventions alongside a robust through reimbursement models, workforce incentives,
clinical care plan. To enhance effectiveness and real-world and investments in infrastructure. Policies that promote
applicability, future research should prioritize clinical- community health worker certification and fund grassroots
community partnerships and design care pathways that innovation through research-practice partnerships will be
span pre-treatment, concurrent treatment, and post- key.
treatment phases, ensuring sustained lifestyle support 7. Conclusion
across the continuum of care. The absence of standardized
outcome measures, core implementation frameworks, and Community-based interventions have become essential in
uniform reporting practices limits the ability to compare addressing the persistent burden and disparities of CVD.
results across studies or conduct robust meta-analyses. Programs grounded in cultural relevance, trust, and local
Many promising programs remain unpublished or infrastructure offer scalable solutions that extend beyond
unevaluated due to resource constraints, limited research clinical settings. A growing body of evidence supports
infrastructure, and challenges navigating institutional the effectiveness of these interventions across diverse
review board processes. Future efforts should prioritize populations and delivery models. As this evidence base
the development of flexible yet rigorous evaluation models grows, it is now imperative to integrate these approaches
such as hybrid effectiveness-implementation designs and into mainstream healthcare, supported by sustainable
49
the establishment of core outcome sets for community- funding, robust research infrastructure, and policy reform.
based CVD research. This conceptual framework illustrates how a partnership
Furthermore, many community-rooted strategies between academic institutions and community entities can
remain disconnected from guidelines and the broader contribute distinct but complementary resources that feed
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 56 doi: 10.36922/GTM025170040