Page 88 - IJAMD-1-2
P. 88
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
AMTransformer for process dynamics
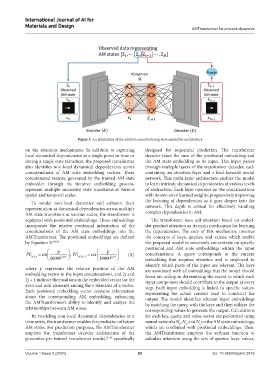
Figure 5. An illustration of the additive manufacturing state embedder architecture
on the attention mechanisms. In addition to capturing designed for sequential prediction. The transformer
local dynamical dependencies at a single point in time or decoder takes the sum of the positional embedding and
during a single state transition, the proposed transformer the AM state embedding as its input. This input passes
also identifies non-local dynamical dependencies across through multiple layers of the transformer decoder, each
concatenations of AM state embedding vectors. These containing an attention layer and a feed-forward neural
concatenated vectors, generated by the trained AM state network. This multi-layer architecture enables the model
embedder through its iterative embedding process, to learn intricate dynamical dependencies at various levels
represent multiple successive state transitions at various of abstraction. Each layer operates on the concatenations
spatial and temporal scales. with its own set of learned weights, progressively improving
To model non-local dynamics and enhance their the learning of dependencies as it goes deeper into the
representation as dynamical dependencies across multiple network. This depth is critical for effectively handling
AM state transitions at various scales, the transformer is complex dependencies in AM.
equipped with positional embeddings. These embeddings The transformer uses self-attention based on scaled-
incorporate the relative positional information of the dot product attention as its main mechanism for learning
concatenations of the AM state embeddings into the the dependencies. The core of this mechanism involves
AMTransformer. The positional embeddings are defined the concepts of keys, queries, and values, which enable
by Equation X: 28,32 the proposed model to selectively concentrate on specific
positional and AM state embeddings within the input
p p
PE = sin , PE = cos (X) concatenations. A query corresponds to the current
p , 2 j 2/je 10000 p +1 , 2 j 2/je 10000 embedding that requires attention and is employed to
identify which parts of the input are relevant. The keys
where p represents the relative position of the AM are associated with all embeddings that the model should
embedding vector in the input concatenations, and 2j and focus on, aiding in determining the extent to which each
2j + 1 indicate the positions in the embedded vector for the input component should contribute to the output at every
even and odd elements among the e elements of a vector. step. Each input embedding is linked to specific values,
Each positional embedding vector contains information representing the actual content used to construct the
about the corresponding AM embedding, enhancing output. The model identifies relevant input embeddings
the AMTransformer’s ability to identify and analyze the by matching the query with the keys and then utilizes the
relationships between AM states. corresponding values to generate the output. Calculations
By modeling non-local dynamical dependencies in a for each key, query, and value vector are performed using
time series, the transformer enables the prediction of future neural networks N , N , and N on the AM state embeddings,
v
q
k
AM states. For prediction purposes, the AMTransformer which are combined with positional embeddings. Then,
employs the transformer decoder architecture of the the AMTransformer employs the softmax function to
generative pre-trained transformer model, 36-38 specifically calculate attention using the sets of queries, keys, values,
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 82 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.3919