Page 44 - IJAMD-1-3
P. 44
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Metal AM porosity prediction using ML
A B
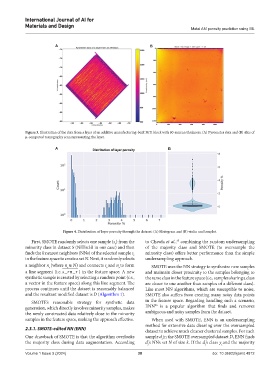
Figure 3. Illustration of the data from a layer of an additive manufacturing-built NiTi block with 60-micron thickness. (A) Pyrometer data and (B) slice of
µ-computed tomography scan representing the layer.
A B
Figure 4. Distribution of layer porosity through the dataset: (A) Histogram and (B) violin and boxplot.
First, SMOTE randomly selects one sample (s ) from the to Chawla et al., combining the random undersampling
35
r
minority class in dataset S (NiTi×3B in our case) and then of the majority class and SMOTE (to oversample the
finds the k nearest neighbors (NNs) of the selected sample s r minority class) offers better performance than the simple
in the feature space to create a set N. Next, it randomly selects undersampling approach.
a neighbor n (where n ∈ N) and connects s and n to form SMOTE uses the NN strategy to synthesize new samples
r
r
r
r
a line segment (i.e. _ _ s rn r ) in the feature space. A new and maintain closer proximity to the samples belonging to
synthetic sample is created by selecting a random point (i.e., the same class in the feature space (i.e., samples sharing a class
a vector in the feature space) along this line segment. The are closer to one another than samples of a different class).
process continues until the dataset is reasonably balanced Like most NN algorithms, which are susceptible to noise,
and the resultant modified dataset is D (Algorithm 1). SMOTE also suffers from creating many noisy data points
SMOTE’s reasonable strategy for synthetic data in the feature space. Regarding handling such a scenario,
36
generation, which directly involves minority samples, makes ENN is a popular algorithm that finds and removes
the newly constructed data relatively close to the minority ambiguous and noisy samples from the dataset.
samples in the feature space, making the approach effective. When used with SMOTE, ENN is an undersampling
method for extensive data cleaning over the oversampled
2.3.1. SMOTE-edited NN (ENN) dataset to achieve much cleaner clustered samples. For each
One drawback of SMOTE is that the algorithm overlooks sample d in the SMOTE oversampled dataset D, ENN finds
i
the majority class during data augmentation. According d’s NNs set N of size k. If the d’s class y and the majority
i
i
i
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 38 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.4812