Page 49 - IJAMD-1-3
P. 49
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Metal AM porosity prediction using ML
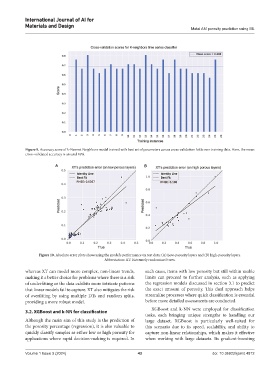
Figure 9. Accuracy score of k-Nearest Neighbors model trained with best set of parameters across cross-validation folds over training data. Here, the mean
cross‑validated accuracy is around 69%.
A B
Figure 10. Absolute error plots showcasing the model’s performance on test data: (A) Low-porosity layers and (B) high-porosity layers.
Abbreviation: XT: Extremely randomized trees.
whereas XT can model more complex, non-linear trends, such cases, items with low porosity but still within usable
making it a better choice for problems where there is a risk limits can proceed to further analysis, such as applying
of underfitting or the data exhibits more intricate patterns the regression models discussed in section 3.1 to predict
that linear models fail to capture. XT also mitigates the risk the exact amount of porosity. This dual approach helps
of overfitting by using multiple DTs and random splits, streamline processes where quick classification is essential
providing a more robust model. before more detailed assessments are conducted.
XGBoost and k-NN were employed for classification
3.2. XGBoost and k-NN for classification
tasks, each bringing unique strengths to handling our
Although the main aim of this study is the prediction of large dataset. XGBoost is particularly well-suited for
the porosity percentage (regression), it is also valuable to this scenario due to its speed, scalability, and ability to
quickly classify samples as either low or high porosity for capture non-linear relationships, which makes it effective
applications where rapid decision-making is required. In when working with large datasets. Its gradient-boosting
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 43 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.4812