Page 102 - IJB-10-1
P. 102
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting for musculoskeletal system
exploring molecular mechanisms and screening drug chronic and degenerative disease that is increasingly
candidates for MSDs (Table 5). Metabolic bone disease prevalent in aging and obese populations. Little is
200
(MBD) encompasses a broad spectrum of conditions known in the case of the molecular mechanisms of the
characterized by abnormalities in bone mineral or bone onset and progression of osteoarthritis, and thus, most
matrix, affecting over 500 million people worldwide. current treatments for osteoarthritis alleviate symptoms
196
Among them, osteoporosis is the most common and without repairing the cartilage tissues. Understanding the
associated with high risk of fractures. To better understand interaction between osteochondral tissues, symptoms,
197
the bone metabolic pathologies and to develop therapeutic and related signaling pathways will provide better
drugs, in vitro models of bone tissue are urgently needed. options for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Toward this,
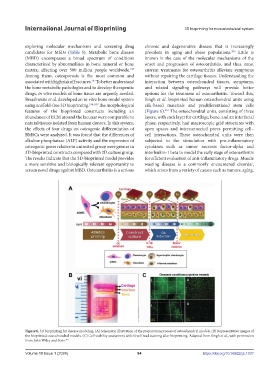
Breathwaite et al. developed an in vitro bone model system Singh et al. bioprinted human osteochondral units using
using scaffold-free 3D bioprinting. 198,199 The morphological silk-based materials and predifferentiated stem cells
features of the bioprinted constructs including an (Figure 6). The osteochondral units, consisting of three
201
abundance of ECM around the lacunar were comparable to layers, with each layer for cartilage, bone, and an interfacial
natural tissues isolated from human donors. In this system, phase, respectively, had macroscopic grid structures with
the effects of four drugs on osteogenic differentiation of open spaces and interconnected pores permitting cell–
BMSCs were analyzed. It was found that the differences of cell interactions. These osteochondral units were then
alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and the expression of subjected to the stimulation with pro-inflammatory
osteogenic genes relative to untreated group were greater in cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and
3D-bioprinted constructs compared with 2D culture group. interleukin-1 beta to model the early stage of osteoarthritis
The results indicate that the 3D-bioprinted model provides for efficient evaluation of anti-inflammatory drugs. Muscle
a more sensitive and biologically relevant opportunity to wasting disease is a commonly encountered disorder,
screen novel drugs against MBD. Osteoarthritis is a serious which arises from a variety of causes such as tumors, aging,
Figure 6. 3D bioprinting for disease modeling. (A) Schematic illustration of the preparation process of osteochondral models. (B) Representative images of
the bioprinted osteochondral models. (C) Cell viability assessment with Live/Dead staining after bioprinting. Adapted from Singh et al., with permission
from John Wiley and Sons. 201
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 94 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1037