Page 170 - IJB-10-1
P. 170
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinted cell-laden hydrogel for tracheal application
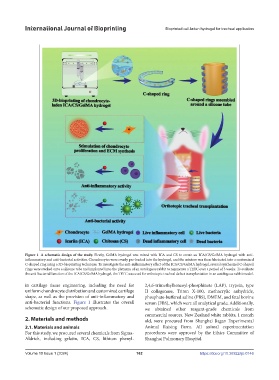
Figure 1. A schematic design of the study. Firstly, GelMA hydrogel was mixed with ICA and CS to create an ICA/CS/GelMA hydrogel with anti-
inflammatory and anti-bacterial activities. Chondrocytes were evenly pre-loaded into the hydrogel, and the mixture was then fabricated into a customized
C-shaped ring using a 3D-bioprinting technique. To investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of the ICA/CS/GelMA hydrogel, several synthesized C-shaped
rings were stacked onto a silicone tube and implanted into the platysma of an autologous rabbit to regenerate a TETC over a period of 3 weeks. To evaluate
the anti-bacterial function of the ICA/CS/GelMA hydrogel, the TETC was used for orthotopic tracheal defect transplantation in an autologous rabbit model.
in cartilage tissue engineering, including the need for 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl-phosphinate (LAP), trypsin, type
uniform chondrocyte distribution and customized cartilage II collagenase, Triton X-100, methacrylic anhydride,
shape, as well as the provision of anti-inflammatory and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), DMEM, and fetal bovine
anti-bacterial functions. Figure 1 illustrates the overall serum (FBS), which were all analytical grade. Additionally,
schematic design of our proposed approach. we obtained other reagent-grade chemicals from
commercial sources. New Zealand white rabbits, 1 month
2. Materials and methods old, were procured from Shanghai Jiagan Experimental
2.1. Materials and animals Animal Raising Farm. All animal experimentation
For this study, we procured several chemicals from Sigma- procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of
Aldrich, including gelatin, ICA, CS, lithium phenyl- Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital.
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 162 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0146