Page 175 - IJB-10-1
P. 175
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinted cell-laden hydrogel for tracheal application
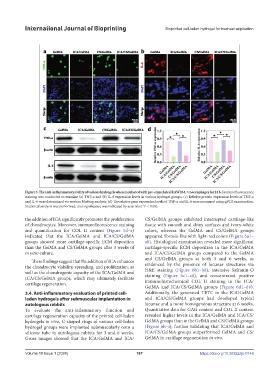
Figure 3. The anti-inflammatory ability of various hydrogels when incubated with pre-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages for 24 h. Immunofluorescence
staining was conducted to examine (a) TNF-α and (b) IL-6 expression levels in various hydrogel groups. (c) Relative protein expression levels of TNF-α
and IL-6 were determined via western blotting analysis. (d) The relative gene expression levels of TNF-α and IL-6 were measured using qPCR examination.
Statistical analysis was performed, and significance was indicated by asterisks (*P < 0.05).
the addition of ICA significantly promotes the proliferation CS/GelMA groups exhibited interrupted cartilage-like
of chondrocytes. Moreover, immunofluorescence staining tissue with smooth and shiny surfaces and ivory-white
and quantification for COL II content (Figure 5d–e) colors, whereas the GelMA and CS/GelMA groups
indicated that the ICA/GelMA and ICA/CS/GelMA appeared fibrosis-like with light-red colors (Figure 6a1–
groups showed more cartilage-specific ECM deposition a8). Histological examination revealed more significant
than the GelMA and CS/GelMA groups after 3 weeks of cartilage-specific ECM deposition in the ICA/GelMA
in vitro culture. and ICA/CS/GelMA groups compared to the GelMA
and CS/GelMA groups at both 3 and 6 weeks, as
These findings suggest that the addition of ICA enhances
the chondrocyte viability, spreading, and proliferation, as evidenced by the presence of lacunar structures via
H&E staining (Figure 6b1–b8), intensive Safranin-O
well as the chondrogenic capacity of the ICA/GelMA and staining (Figure 6c1–c8), and concentrated positive
ICA/CS/GelMA groups, which may ultimately facilitate immunohistochemical COL II staining in the ICA/
cartilage regeneration.
GelMA and ICA/CS/GelMA groups (Figure 6d1–d8).
3.4. Anti-inflammatory evaluation of printed cell- Additionally, the generated TETC in the ICA/GelMA
laden hydrogels after submuscular implantation in and ICA/CS/GelMA groups had developed typical
autologous rabbits lacunae and a more homogeneous structure at 6 weeks.
To evaluate the anti-inflammatory function and Quantitative data for GAG content and COL II content
cartilage regeneration capacity of the printed cell-laden revealed higher levels in the ICA/GelMA and ICA/CS/
hydrogels in vivo, C-shaped rings of various cell-laden GelMA groups than in the GelMA and CS/GelMA groups
hydrogel groups were implanted submuscularly onto a (Figure 6h–i), further validating that ICA/GelMA and
silicone tube in autologous rabbits for 3 and 6 weeks. ICA/CS/GelMA groups outperformed GelMA and CS/
Gross images showed that the ICA/GelMA and ICA/ GelMA in cartilage regeneration in vivo.
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 167 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0146