Page 176 - IJB-10-1
P. 176
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinted cell-laden hydrogel for tracheal application
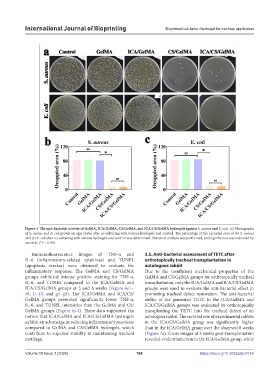
Figure 4. The anti-bacterial activity of GelMA, ICA/GelMA, CS/GelMA, and ICA/CS/GelMA hydrogels against S. aureus and E. coli. (a) Photographs
of S. aureus and E. coli grown on agar plates after co-culturing with various hydrogels and control. The percentage of the occupied area of (b) S. aureus
and (c) E. coli after co-culturing with various hydrogels and control was determined. Statistical analysis was performed, and significance was indicated by
asterisks (*P < 0.05).
Immunofluorescence images of TNF-α and 3.5. Anti-bacterial assessment of TETC after
IL-6 (inflammatory-related cytokines) and TUNEL orthotopically tracheal transplantation in
(apoptosis marker) were obtained to evaluate the autologous rabbit
inflammatory response. The GelMA and CS/GelMA Due to the insufficient mechanical properties of the
groups exhibited intense positive staining for TNF-α, GelMA and CS/GelMA groups for orthotopically tracheal
IL-6, and TUNEL compared to the ICA/GelMA and transplantation, only the ICA/GelMA and ICA/CS/GelMA
ICA/CS/GelMA groups at 3 and 6 weeks (Figure 6e1– groups were used to evaluate the anti-bacterial effect in
e8, f1–f8, and g1–g8). The ICA/GelMA and ICA/CS/ promoting tracheal defect restoration. The anti-bacterial
GelMA groups presented significantly lower TNF-α, ability of the generated TETC in the ICA/GelMA and
IL-6, and TUNEL intensities than the GelMA and CS/ ICA/CS/GelMA groups was evaluated by orthotopically
GelMA groups (Figure 6j–l). These data supported the transplanting the TETC into the tracheal defect of an
notion that ICA/GelMA and ICA/CS/GelMA hydrogels autologous rabbit. The survival rate of experimental rabbits
exhibit an advantage in reducing inflammatory reactions in the ICA/CS/GelMA group was significantly higher
compared to GelMA and CS/GelMA hydrogels, which than in the ICA/GelMA group over the observed 8 weeks
contribute to superior stability in maintaining tracheal (Figure 7a). Gross images at 3 weeks post-transplantation
cartilage. revealed evident infection in the ICA/GelMA group, while
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 168 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0146