Page 178 - IJB-10-1
P. 178
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinted cell-laden hydrogel for tracheal application
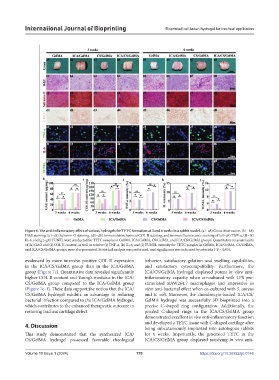
Figure 6. The anti-inflammatory effect of various hydrogels for TETC formation at 3 and 6 weeks in a rabbit model. (a1–a8) Gross observation, (b1–b8)
H&E staining, (c1–c8) Safranin-O staining, (d1–d8) immunohistochemical COL II staining, and immunofluorescence staining of (e1–e8) TNF-α, (f1–f8)
IL-6, and (g1–g8) TUNEL were conducted for TETC samples in GelMA, ICA/GelMA, CS/GelMA, and ICA/CS/GelMA groups. Quantitative measurements
of (h) GAG and (i) COL II content, as well as relative (j) TNF-α, (k) IL-6, and (l) TUNEL intensity for TETC samples in GelMA, ICA/GelMA, CS/GelMA,
and ICA/CS/GelMA groups were also presented. Statistical analysis was performed, and significance was indicated by asterisks (*P < 0.05).
evidenced by more intensive positive COL II expression behavior, satisfactory gelation and swelling capabilities,
in the ICA/CS/GelMA group than in the ICA/GelMA and satisfactory cytocompatibility. Furthermore, the
group (Figure 7c). Quantitative data revealed significantly ICA/CS/GelMA hydrogel displayed potent in vitro anti-
higher COL II content and Young’s modulus in the ICA/ inflammatory capacity when co-cultured with LPS pre-
CS/GelMA group compared to the ICA/GelMA group stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages and impressive in
(Figure 7e–f). These data support the notion that the ICA/ vitro anti-bacterial effect when co-cultured with S. aureus
CS/GelMA hydrogel exhibits an advantage in reducing and E. coli. Moreover, the chondrocyte-loaded ICA/CS/
bacterial infection compared to the ICA/GelMA hydrogel, GelMA hydrogel was successfully 3D bioprinted into a
which contributes to the enhanced therapeutic outcome in precise C-shaped ring configuration. Additionally, the
restoring tracheal cartilage defect. printed C-shaped rings in the ICA/CS/GelMA group
demonstrated excellent in vivo anti-inflammatory function
and developed a TETC tissue with C-shaped cartilage after
4. Discussion being subcutaneously implanted into autologous rabbits
This study demonstrated that the synthesized ICA/ for 6 weeks. Importantly, the generated TETC in the
CS/GelMA hydrogel possessed favorable rheological ICA/CS/GelMA group displayed satisfying in vivo anti-
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 170 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0146