Page 218 - IJB-10-1
P. 218
International Journal of Bioprinting CS-laden microporous bio-ink for cartilage regeneration
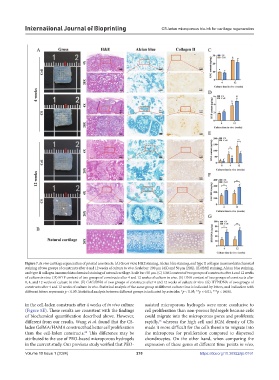
Figure 7. In vivo cartilage regeneration of printed constructs. (A) Gross view, H&E staining, Alcian blue staining, and type II collagen immunohistochemical
staining of two groups of constructs after 4 and 12 weeks of culture in vivo. Scale bar: 200 μm (4X) and 50 μm (20X). (B) H&E staining, Alcian blue staining,
and type II collagen immunohistochemical staining of natural cartilage. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) GAG content of two groups of constructs after 4 and 12 weeks
of culture in vivo. (D) HYP content of two groups of constructs after 4 and 12 weeks of culture in vivo. (E) DNA content of two groups of constructs after
0, 4, and 12 weeks of culture in vivo. (F) GAG/DNA of two groups of constructs after 4 and 12 weeks of culture in vivo. (G) HYP/DNA of two groups of
constructs after 4 and 12 weeks of culture in vivo. Statistical analysis of the same group at different culture time is indicated by letters, and indication with
different letters represents p < 0.05. Statistical analysis between different groups is indicated by asterisks: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
in the cell-laden constructs after 4 weeks of in vivo culture assisted microporous hydrogels were more conducive to
(Figure 8E). These results are consistent with the findings cell proliferation than non-porous hydrogels because cells
of biochemical quantification described above. However, could migrate into the microporous pores and proliferate
different from our results, Wang et al. found that the CS- rapidly, whereas the high cell and ECM density of CSs
26
laden GelMA/HAMA construct had better cell proliferation made it more difficult for the cells therein to migrate into
than the cell-laden constructs. This difference may be the micropores for proliferation compared to dispersed
20
attributed to the use of PEO-based microporous hydrogels chondrocytes. On the other hand, when comparing the
in the current study. Our previous study verified that PEO- expression of these genes at different time points in vivo,
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 210 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0161