Page 512 - IJB-10-1
P. 512
International Journal of Bioprinting Macro and micro structure of a 3D-printed implant
study on artificial prosthetic femur after high tibial to the contralateral cortical bone prior to the experiment.
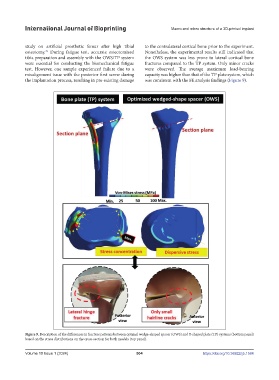
osteotomy. During fatigue test, accurate osteotomized Nonetheless, the experimental results still indicated that
39
tibia preparation and assembly with the OWS/TP system the OWS system was less prone to lateral cortical bone
were essential for conducting the biomechanical fatigue fractures compared to the TP system. Only minor cracks
test. However, one sample experienced failure due to a were observed. The average maximum load-bearing
misalignment issue with the posterior first screw during capacity was higher than that of the TP plate system, which
the implantation process, resulting in pre-existing damage was consistent with the FE analysis findings (Figure 9).
Figure 9. Description of the differences in fracture patterns between optimal wedge-shaped spacer (OWS) and T-shaped plate (TP) systems (bottom panel)
based on the stress distributions on the cross-section for both models (top panel).
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 504 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1584