Page 92 - IJB-10-1
P. 92
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting for musculoskeletal system
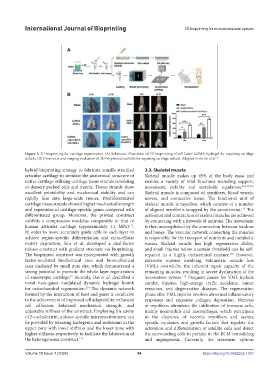
Figure 2. 3D bioprinting for cartilage regeneration. (A) Schematic illustration of 3D bioprinting of cell-laden GelMA hydrogel for repairing cartilage
defects. (B) Gross view and imaging evaluation of 3D-bioprinted scaffolds for repairing cartilage defects. Adapted from Pei et al. 111
hybrid bioprinting strategy to fabricate zonally stratified 3.3. Skeletal muscle
articular cartilage to simulate the anatomical structure of Skeletal muscle makes up 45% of the body mass and
native cartilage utilizing cartilage tissue strands consisting enables a variety of vital functions including support,
of densely packed cells and matrix. Tissue strands show movement, stability and metabolic regulation. 25,115,116
excellent printability and mechanical stability and can Skeletal muscle is composed of myofibers, blood vessels,
rapidly fuse into large-scale tissues. Predifferentiated nerves, and connective tissue. The functional unit of
cartilage tissue strands showed higher mechanical strength skeletal muscle is myofiber, which consists of a number
and expression of cartilage-specific genes compared with of aligned myofibrils wrapped by the sarcolemma. The
117
differentiated group. Moreover, the printed construct activation and contraction of skeletal muscles are achieved
exhibits a compression modulus comparable to that of by connecting with a network of neurons. The movement
113
human articular cartilage (approximately 1.1 MPa) . is then accomplished by the connection between tendons
In order to more accurately guide cells in each layer to and bones. The vascular network connecting the muscles
achieve region-specific differentiation and extracellular is responsible for the transport of nutrients and metabolic
matrix deposition, Sun et al. developed a dual-factor wastes. Skeletal muscle has high regenerative ability,
release construct with gradient structure via bioprinting. and small injuries below a certain threshold can be self-
The bioprinted construct was incorporated with growth repaired in a highly orchestrated manner. However,
118
factor-mediated biochemical cues and biomechanical extensive injuries involving volumetric muscle loss
cues mediated by small pore size, which demonstrated a (VML) overwhelm the inherent repair capacity of the
strong potential to promote the whole-layer regeneration remaining muscles, resulting in severe dysfunction of the
of anisotropic cartilage. Recently, Dai et al. described a locomotion system. Frequent causes for VML include
87
119
novel host–guest modulated dynamic hydrogel bioink combat injuries, high-energy traffic accidents, tumor
for osteochondral regeneration. The dynamic network resection, and degenerative diseases. The regeneration
114
formed by the interaction of host and guest is conducive phase after VML injuries involves abnormal inflammatory
to the achievement of improved cell adaptability, enhanced responses and excessive collagen deposition. Necrosis
cell adhesion, bolstered mechanical strength, and of myofibers stimulates the infiltration of immune cells,
adjustable stiffness of the construct. Employing the cavity mainly neutrophils and macrophages, which participate
of β-cyclodextrin, a tissue-specific microenvironment can in the clearance of necrotic myofibers and secrete
be provided by releasing kartogenin and melatonin in the specific cytokines and growth factors that regulate the
upper zone with lower stiffness and the lower zone with activation and differentiation of satellite cells and direct
higher stiffness, respectively, to facilitate the fabrication of the surrounding cells to partake in the ECM remodeling
the heterogeneous construct. 114 and angiogenesis. Currently, the treatment options
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 84 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1037