Page 228 - IJB-10-2
P. 228
International Journal of Bioprinting Property of scaffolds with different lattices
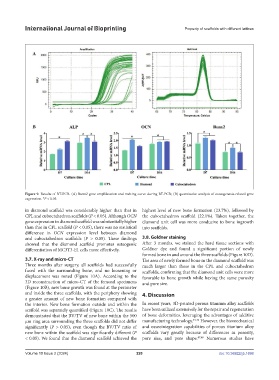
Figure 9. Results of RT-PCR. (A) Runx2 gene amplification and melting curve during RT-PCR; (B) quantitative analysis of osteogenesis-related gene
expression. *P < 0.05.
in diamond scaffold was considerably higher than that in highest level of new bone formation (23.7%), followed by
CPL and cuboctahedron scaffolds (P < 0.05). Although OCN the cuboctahedron scaffold (22.1%). Taken together, the
gene expression in diamond scaffold was substantially higher diamond unit cell was more conducive to bone ingrowth
than that in CPL scaffold (P < 0.05), there was no statistical into scaffolds.
difference in OCN expression level between diamond
and cuboctahedron scaffolds (P > 0.05). These findings 3.8. Goldner staining
showed that the diamond scaffold promotes osteogenic After 3 months, we stained the hard tissue sections with
differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells more effectively. Goldner dye and found a significant portion of newly
formed bone in and around the three scaffolds (Figure 10D).
3.7. X-ray and micro-CT The area of newly formed bone in the diamond scaffold was
Three months after surgery, all scaffolds had successfully much larger than those in the CPL and cuboctahedron
fused with the surrounding bone, and no loosening or scaffolds, confirming that the diamond unit cells were more
displacement was noted (Figure 10A). According to the favorable to bone growth while having the same porosity
3D reconstruction of micro-CT of the femoral specimens and pore size.
(Figure 10B), new bone growth was found at the perimeter
and inside the three scaffolds, with the periphery showing 4. Discussion
a greater amount of new bone formation compared with
the interior. New bone formation outside and within the In recent years, 3D-printed porous titanium alloy scaffolds
scaffold was separately quantified (Figure 10C). The results have been utilized extensively for the repair and regeneration
demonstrated that the BV/TV of new bone within the 500 of bone deformities, leveraging the advantages of additive
μm ring area surrounding the three scaffolds did not differ manufacturing technology. 44-46 However, the biomechanical
significantly (P > 0.05), even though the BV/TV ratio of and osseointegration capabilities of porous titanium alloy
new bone within the scaffold was significantly different (P scaffolds vary greatly because of differences in porosity,
< 0.05). We found that the diamond scaffold achieved the pore size, and pore shape. 47,48 Numerous studies have
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 220 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1698