Page 379 - IJB-10-2
P. 379
International Journal of Bioprinting AM evaluation of medical device companies
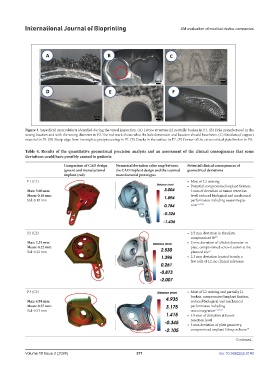
Figure 3. Superficial macrodefects identified during the visual inspection. (A) Lattice structure L2 partially broken in P1. (B) Hole manufactured in the
wrong location and with the wrong diameter in P2. The red mark shows what the hole dimension and location should have been. (C) Residues of support
material in P3. (D) Sharp edge from incomplete postprocessing in P7. (E) Cracks in the surface in P7. (F) Corner of the extra cortical plate broken in P8.
Table 4. Results of the quantitative geometrical precision analysis and an assessment of the clinical consequences that some
deviations could have possibly caused in patients
Comparison of CAD design Numerical deviation color map between Potential clinical consequences of
(green) and manufactured the CAD implant design and the scanned geometrical deviations
implant (red) manufactured prototypes
P1 (C1) • Most of L2 missing
• Potential compromised implant fixation,
Max: 3.00 mm 3 mm of deviation at tumor resection
Mean: 0.16 mm level, reduced biological and mechanical
Std: 0.19 mm performance including osseointegra-
tion 15,22,23
P2 (C2) • 2.5 mm deviation in the plate,
compromised fit 15
Max: 2.53 mm • 2 mm deviation of a hole’s diameter in
Mean: 0.22 mm plate, compromised screw fixation at the
Std: 0.22 mm planned site 15
• 2.3 mm deviation located in only a
few cells of L2, no clinical relevance
P3 (C3) • Most of L2 missing and partially L1
broken, compromised implant fixation,
Max: 4.94 mm reduced biological and mechanical
Mean: 0.37 mm performance including
Std: 0.53 mm osseointegration 15,22,23
• 4.9 mm of deviation at tumor
resection level
• 3 mm deviation of plate geometry,
compromised implant fitting on bone 15
Continued...
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 371 doi: 10.36922/ijb.0140