Page 70 - IJB-4-2
P. 70
Arab W, et al.
3.2 Biocompatibility Studies with different concentrations of both peptides. Our
results revealed that there was no significant cytotoxicity
3.2.1 Cell Viability Results (MTT Assay) induced by the peptide hydrogels (Figures 3B and C)
compared to alginate-gelatin (Figure 3A).
The biocompatibility of both peptides was evaluated
by testing cell proliferation after 24-h incubation with 3.2.3 Cell proliferation and ATP Production in 3D
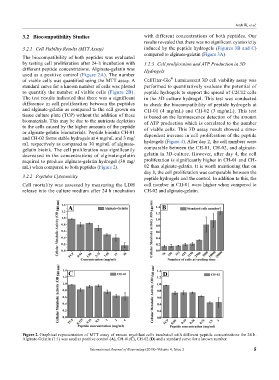
different peptide concentrations. Alginate-gelatin was Hydrogels
used as a positive control (Figure 2A). The number
®
of viable cells was quantified using the MTT assay. A CellTiter-Glo Luminescent 3D cell viability assay was
standard curve for a known number of cells was plotted performed to quantitatively evaluate the potential of
to quantify the number of viable cells (Figure 2B). peptide hydrogels to support the spread of C2C12 cells
The test results indicated that there was a significant in the 3D culture hydrogel. This test was conducted
difference in cell proliferation between the peptides to check the biocompatibility of peptide hydrogels at
and alginate-gelatin as compared to the cell grown on CH-01 (4 mg/mL) and CH-02 (3 mg/mL). This test
tissue culture plate (TCP) without the addition of these is based on the luminescence detection of the amount
biomaterials. This may be due to the nutrients depletion of ATP production which is correlated to the number
to the cells caused by the higher amounts of the peptide of viable cells. This 3D assay result showed a time-
or alginate-gelatin biomaterials. Peptide bioinks CH-01 dependent increase in cell proliferation of the peptide
and CH-02 forms stable hydrogels at 4 mg/mL and 3 mg/
mL respectively as compared to 30 mg/mL of alginate- hydrogels (Figure 4). After day 2, the cell numbers were
gelatin bioink. The cell proliferation was significantly comparable between the CH-01, CH-02, and alginate-
decreased in the concentrations of alginate-gelatin gelatin in 3D-culture. However, after day 4, the cell
required to produce alginate-gelatin hydrogel (30 mg/ proliferation is significantly higher in CH-01 and CH-
mL) when compared to both peptides (Figure 2). 02 than alginate-gelatin. It is worth mentioning that on
day 8, the cell proliferation was comparable between the
3.2.2 Peptides Cytotoxicity peptide hydrogels and the control. In addition to this, the
Cell mortality was assessed by measuring the LDH cell number in CH-01 were higher when compared to
release into the culture medium after 24 h incubation CH-02 and alginate-gelatin.
Figure 2. Graphical representation of MTT assay of mouse myoblast cells incubated with different peptide concentrations for 24 h.
Alginate-Gelatin (1:1) was used as positive control (A), CH-01(C), CH-02 (D) and a standard curve for a known number.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2018)–Volume 4, Issue 2 5