Page 184 - IJB-10-4
P. 184
International Journal of Bioprinting Effects of structure on the interbody cage
to the success of the procedure. The blank control samples CO atmosphere for 1, 4, and 7 days, with medium changes
2
(group without SBF immersion degradation) were immersed every day. After the incubation period, the supernatant was
in distilled water at 37°C for 60 min of state conditioning, and discarded, and a PBS wash was performed. Subsequently, 500
then removed from the distilled water for direct mechanical μL of medium containing 10% Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-
testing. The experimental group sample was removed from 8, Invigentech, USA) was added to each well. The cells were
the immersion solution and then placed in distilled water at further cultured for 2 h in an incubator at 37°C. Finally, the
37°C for 60 min of state conditioning for direct mechanical absorbance at 450 nm was measured using an ELISA reader.
testing, and the samples should be kept in a wet state during
the test. To avoid the test sample sliding in the fixture, the 3. Results and discussion
end parts of the samples face and other items were dried with 3.1. Structural design and modeling of the
paper towels. The uniaxial compression test was carried out interbody fusion cage
by utilizing a universal testing machine: the compression Since the form and structure of the test samples may impact
rate was 1 mm/min; the height was 5 mm; and the the degradation process of the samples, the test samples
compression percentage was 60%. The compressive strength should be comparable to the shape and structure of the
and compressive modulus of the samples before and after final product to ensure the reliability of the experimental
degradation of various structures were eventually obtained. results. For the convenience of the mechanical tests, the
2.4. Cell viability assay interbody fusion cage was simplified by planarizing the
The complete cell culture medium was prepared by upper and lower surfaces of the sample. In order to ensure
mixing Minimum Essential Medium (MEM, Corning, the stability of the interbody fusion cage after implantation,
USA) with fetal bovine serum (FBS, Procell, China) at a the outer contour of the interbody fusion cage should be as
ratio of 9:1. Additionally, 1% of antibiotics (penicillin large as possible. At the same time, it should not exceed
and streptomycin, P/S) were added. MG-63 cells (iCell the outer contour line of the vertebral body to avoid the
Bioscience Inc., Shanghai, China) were cultured in an compression of the surrounding tissues, and the interbody
fusion cage should be placed in a flatter area of the cone.
incubator at 37℃ with a 5% CO atmosphere. Since most patients with cervical spondylosis, according to
2
Different masses (100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg) of PCL raw epidemiologic surveys and hospital data, are affected by a
materials and PCL/HA composite materials, as well as cages pathological condition in the C5/6 segment, the design of
with different structural characteristics, were separately the cage in this study was based on the external morphology
placed in 24-well plates after sterilization using ultraviolet of the endplate surface of the C6 cone. The cross-sectional
light. Three specimens were tested for each sample. MG-63 profile of the designed interbody fusion cage is shown in
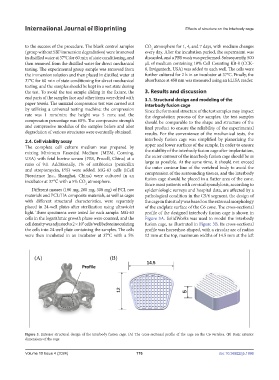
cells in the logarithmic growth phase were counted, and the Figure 3A. SolidWorks was used to model the interbody
cell density was adjusted to 2 × 10 cells/well before inoculating fusion cage, as illustrated in Figure 3B. Its cross-sectional
4
the cells into 24-well plate containing the samples. The cells profile was horseshoe-shaped, with a circular arc of radius
were then incubated in an incubator at 37°C with a 5% 12 mm at the top, maximum widths of 14.5 mm at the left
Figure 3. Exterior structural design of the interbody fusion cage. (A) The cross-sectional profile of the cage on the C6 vertebra. (B) Basic exterior
dimensions of the cage.
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 176 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1996