Page 296 - IJB-10-4
P. 296
International Journal of Bioprinting Analysis of PVA-silk fibroin stents
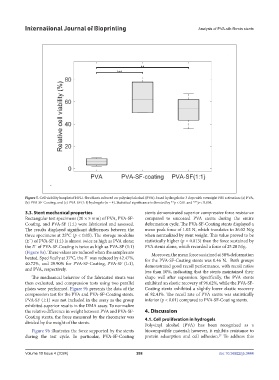
Figure 5. Cell viability boxplot of HFL1 fibroblasts cultured on polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-based hydrogels for 3 days with overnight FBS activation: (a) PVA,
(b) PVA-SF-Coating, and (c) PVA-SF (1:1) hydrogels (n = 4). Statistical significance is denoted by **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.
3.3. Stent mechanical properties stents demonstrated superior compressive force resistance
Rectangular test specimens (20 × 5 mm) of PVA, PVA-SF- compared to uncoated PVA stents during the entire
Coating, and PVA-SF (1:1) were fabricated and assessed. deformation cycle. The PVA-SF-Coating stents displayed a
The results displayed significant differences between the mean peak force of 1.02 N, which translates to 36.02 N/g
three specimens at 25°C (p < 0.05). The storage modulus when normalized by stent weight. This value proved to be
(E´) of PVA-SF (1:1) is almost twice as high as PVA alone; statistically higher (p = 0.013) than the force sustained by
the E´ of PVA-SF-Coating is twice as high as PVA-SF (1:1) PVA stents alone, which recorded a force of 25.20 N/g.
(Figure 9a). These values are reduced when the samples are Moreover, the mean force sustained at 50% deformation
heated. Specifically at 37°C, the E´ was reduced by 42.47%, for the PVA-SF-Coating stents was 0.46 N. Both groups
40.72%, and 29.90% for PVA-SF-Coating, PVA-SF (1:1), demonstrated good recoil performance, with recoil ratios
and PVA, respectively.
less than 10%, indicating that the stents maintained their
The mechanical behavior of the fabricated stents was shape well after expansion. Specifically, the PVA stents
then evaluated, and compression tests using two parallel exhibited an elastic recovery of 96.62%, while the PVA-SF-
plates were performed. Figure 9b presents the data of the Coating stents exhibited a slightly lower elastic recovery
compression test for the PVA and PVA-SF-Coating stents. of 92.41%. The recoil rate of PVA stents was statistically
PVA-SF (1:1) was not included in the assay as the group inferior (p < 0.01) compared to PVA-SF-Coating stents.
exhibited superior results in the DMA assay. To normalize
the relative difference in weight between PVA and PVA-SF- 4. Discussion
Coating stents, the force measured by the rheometer was 4.1. Cell proliferation in hydrogels
divided by the weight of the stents. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) has been recognized as a
Figure 9b illustrates the force supported by the stents biocompatible material; however, it exhibits resistance to
during the test cycle. In particular, PVA-SF-Coating protein adsorption and cell adhesion. To address this
27
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 288 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3444