Page 41 - IJB-10-4
P. 41
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting in otorhinolaryngology
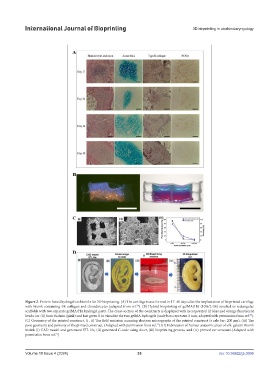
Figure 2. Protein-based hydrogels as bioinks for 3D bioprinting. (A) The cartilage tissue formed in 17–40 days after the implantation of bioprinted cartilage
68
with bioink containing 4% collagen and chondrocytes (adapted from ref. ). (B) Hybrid bioprinting of gelMA/HA (10%/2.4%) resulted in rectangular
scaffolds with two separate gelMA/HA hydrogel parts. The cross-section of the constructs is displayed with incorporated (i) blue and orange fluorescent
70
beads i or (ii) basic fuchsin (pink) and fast green ii to visualize the two gelMA hydrogels (scale bars represent 2 mm; adapted with permission from ref. ).
(C) Geometry of the printed construct. (i , ii) The field emission scanning electron micrographs of the printed construct (s cale bar: 200 μm). (iii) The
75
pore geometry and porosity of the printed construct. (Adapted with permission from ref. ) (D) Fabrication of human anatomical ear of silk-gelatin Bioink
bioink (i) CAD model and generated STL file, (ii) generated G code using slicer, (iii) bioprinting process, and (iv) printed ear structure.(Adapted with
permission from ref. )
75
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 33 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3006