Page 549 - IJB-10-4
P. 549
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-bioprinting of osteochondral plugs
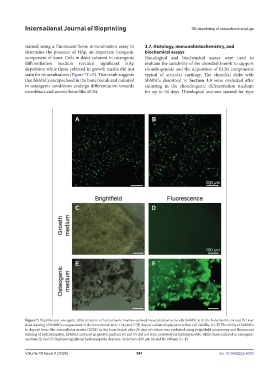
stained using a fluorescent bone mineralization assay to 3.7. Histology, immunohistochemistry, and
determine the presence of HAp, an important inorganic biochemical assays
component of bone. Cells in disks cultured in osteogenic Histological and biochemical assays were used to
differentiation medium revealed significant HAp evaluate the suitability of the chondral bioink to support
deposition while those cultured in growth media did not chondrogenesis and the deposition of ECM components
stain for mineralization (Figure 7C–F). This result suggests typical of articular cartilage. The chondral disks with
that hbMSCs encapsulated in the bone bioink and cultured hbMSCs described in Section 3.5 were evaluated after
in osteogenic conditions undergo differentiation towards culturing in the chondrogenic differentiation medium
osteoblasts and secrete bone-like ECM. for up to 56 days. Histological sections stained for type
Figure 7. Viability and osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hbMSCs) in the bone bioink. (A and B) Live/
dead staining of hbMSCs encapsulated in the bone bioink after 1 (A) and 7 (B) days of culture displayed excellent cell viability. (C–F) The ability of hbMSCs
to deposit bone-like extracellular matrix (ECM) in the bone bioink after 28 days of culture was evaluated using brightfield microscopy and fluorescent
staining of hydroxyapatite. hbMSCs cultured in growth medium (C and D) did not stain positively for hydroxyapatite, while those cultured in osteogenic
medium (E and F) displayed significant hydroxyapatite deposits. Scale bars: 200 µm (A and B); 100 µm (C–F).
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 541 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4053