Page 574 - IJB-10-4
P. 574
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printing silicone patient-specific soft-tissue expander
implants in patients with severe bone atrophy. Several gingival easier and permits more bone gain, both horizontally and
periosteal-releasing techniques for tension-free wound vertically (Figure 1). 2,3
closure have been developed, but these techniques may lead Current hydrogel self-inflating expanders have
1
to insufficient keratinized gingival tissue, flat vestibular depth, several different preformed sizes and shapes. However,
and compromise the prognosis of dental endosseous implants.
For example, secondary vestibuloplasty is commonly the morphology of bone defects is highly individualized,
performed for gingival grafts, but the patient may require a and not all preformed expanders meet the desired final
long-term treatment course and multiple surgeries. 1 morphology. Moreover, the volume increase is not
comparable to the increase in soft-tissue surface. Research
A soft-tissue expander increases the tissue surface for has revealed that the round expander has the largest amount
reconstruction and is frequently used in plastic surgeries, of fractional area gain followed by square, rectangular,
such as breast augmentation and scar revision (e.g., burn and crescent-shaped expanders under the same pressure
injury or skin tumor excision). The traditional soft-tissue applied on the same surface area. It would be ideal if
4
expander is a silicon shell with a port (embedded under the increase in final surface area could be defined in the
the cutaneous tissue) for saline injection. Progressive skin pre-expansion stage, and the area gain fraction would no
inflation is accomplished by saline injection through the longer be an issue for gingival tissue expansion.
port. This injection system is not feasible for small and
thin intraoral gingival tissues, leading to the development A good patient-specific soft-tissue expander must be
of the first self-inflated expander in 2007. In the expander, designed according to the geometric shape of the bone
the hydrogel is introduced into a silicon shell that absorbs defect to maximize the contact area between the expander
body fluid to expand spontaneously. The self-inflated soft- and bone defect hard tissue. It should gradually expand
tissue expander expands the gingival tissue surface before without damaging the soft tissues to meet clinical needs.
bone augmentation and wound closure. This approach is Consequently, the expander material, the expansion agent
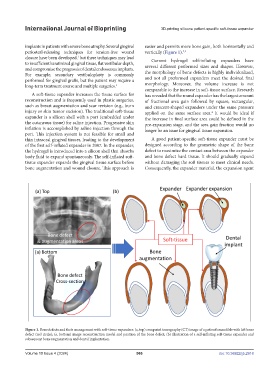
Figure 1. Bone defects and their management with soft-tissue expanders: (a, top) computed tomography (CT) image of a patient’s mandible with left bone
defect (red circle); (a, bottom) image reconstruction model and position of the bone defect; (b) illustration of a self-inflating soft-tissue expander and
subsequent bone augmentation and dental implantation.
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 566 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2918