Page 12 - IJB-5-1
P. 12
Biofabrication offers future hope for tackling various obstacles and challenges in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: A Perspective
technologies for facilitating the precise programmable It is often thought that the in vivo approaches are
designing, computer-controlled efficient biofabrication, physiologically better and look realistic enough.
and post-fabrication incubation are urgently needed. There However, this is not necessarily true and in vivo approaches
is still a long way to go in fabricating bioartificial organs are not always better for organ engineering. One of the main
on demand, but these technologies are achievable. If limitations of in vivo approaches for tissue engineering
biofabrication approaches will work out, it will become research is the regeneration of only fibrous tissues. It
possible to fabricate not only Humanscale patient- has been demonstrated that fibroblasts and inflammatory
specific tissue grafts/organs at a rapid pace (irrespective cells are the most strongly proliferating cells in the living
of organ size) but it will also shorten the time required of body consuming large amount of nutrients and oxygen to
growth performance and development of organs. Then, no provide energy for proliferation of metabolically active
patient will ever have to wait on lengthy transplant lists cells [114-116] . Therefore, the transplanted cells cannot
for donor organs, and no patient will ever have to take survive without a blood supply, sufficient supply of
powerful, debilitating and potentially fatal drugs to treat essential nutrients, or adequate means for waste product
chronic pains and to prevent their immune systems removal. Instead, outside the body, the desired tissues or
from rejecting new body parts or from attacking the organs can be grown without pro-fibrogenic environment.
transplanted organ when the organ is not closely matched. Therefore, better in vitro strategies are really needed to
support, instruct, and maintain cells inside immune-
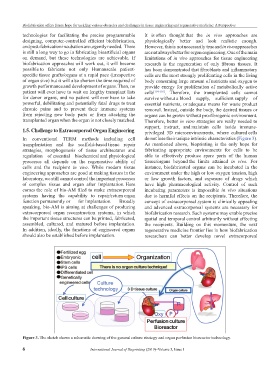
1.5. Challenge to Extracorporeal Organ Engineering privileged 3D microenvironments, where cultured cells
In conventional TERM methods including cell do not lose their unique intrinsic characteristics (Figure 3).
transplantation and the scaffold-based tissue repair As mentioned above, bioprinting is the only hope for
strategies, morphogenesis of tissue architectures and fabricating appropriate environments for cells to be
regulation of essential biochemical and physiological able to effectively produce spare parts of the human
processes all depends on the regenerative ability of tissue/organs beyond the limits attained in vivo. For
cells and the recipient in vivo. While modern tissue instance, biofabricated organs can be incubated in the
engineering approaches are good at making tissues in the environment under the high or low oxygen tension, high
laboratory, we still cannot control the important processes or low growth factors, and exposure of drugs which
of complex tissue and organ after implantation. Here have high pharmacological activity. Control of such
comes the role of bio-AM filed to make extracorporeal incubating parameters is impossible in vivo situations
systems having the capability to repair/return organ due to harmful effects on the recipients. Therefore, the
function permanently or for implantation. Broadly concept of extracorporeal system is clinically appealing
speaking, bio-AM is aiming at challenges of producing and advanced extracorporeal systems are necessary for
extracorporeal organ reconstruction systems, in which biofabrication research. Such systems may enable precise
the important tissue structures can be printed, fabricated, spatial and temporal control arbitrarily without affecting
assembled, cultured, and matured before implantation. the recipients. Building on this momentum, the next
In addition, ideally, the functions of engineered organs regenerative medicine frontier lies in how biofabrication
should also be established before implantation. researchers can better develop novel extracorporeal
Figure 3. The sketch shows a schematic drawing of the general culture strategy and organ perfusion bioreactor technology.
6 International Journal of Bioprinting (2019)–Volume 5, Issue 1