Page 69 - IJB-5-1
P. 69
Gao D, et al.
and range of electric bond number χ are limited between 0
and 1 to avoid growth of kink instability . In conclusion,
[85]
final results disclose that the critical Weber number is not
significantly influenced by the electric parameters at high
Reynolds range . Figure 7 shows experimental values
[85]
of the Reynolds number as a function of the capillary
number and most of the points are in stable cone-jet
region which is above the continuous line (theoretical
critical curves) . At the low Reynold numbers, the stable
[85]
region of the jet is affected by three electric parameters.
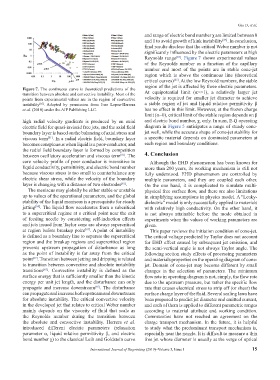
Figure 7. The continuous curve is theoretical predictions of the
transition between absolute and convective instability. Most of the At equipotential limit (α>>1), a relatively larger jet
points from experimental values are in the region of convective velocity is required for smaller jet diameter to achieve
instability . Adapted by permission from Jose Lopez-Herrera a stable region of jet and liquid relative permittivity β
[85]
et al. (2010) under the AIP Publishing LLC. has no effect in this limit. However, at the frozen charge
limit (α=0), critical limit of the stable region depends on β
high radial velocity gradients is produced by an axial and electric bond number, χ, only. In sum, E-Q operating
electric field for quasi-inviscid free jets, and the axial field diagram in Figure 5 anticipates a range of steady cone-
boundary layer is based on the balancing of axial stress and jet well, while the accurate shape of cone-jet stability for
viscous term . In a radial electric field, boundary layer a specific material depends on dominated parameters at
[81]
becomes conspicuous when liquid is a poor-conductor, and each region and boundary conditions.
the radial field boundary layer is formed by competition
between oscillatory acceleration and viscous term . The 4. Conclusion
[81]
core velocity profile of poor conductor is insensitive to Although the EHD phenomenon has been known for
liquid conductivity, permittivity, and electric bond number more than 200 years, its working mechanism is still not
because viscous stress is too small to counterbalance any fully understood. EHD phenomenon are controlled by
electric shear stress, while the velocity of the boundary multiple parameters, and they are coupled each other.
layer is changing with a distance of two electrodes . On the one hand, it is complicated to simulate multi-
[81]
The meniscus may globally be either stable or unstable physical free surface flow, and there are also limitations
up to values of the operational parameters, and the global in simplifying assumptions in physics model. A “Leaky-
stability of the liquid meniscus is a prerequisite for steady dielectric” model is only successfully applied to materials
jetting . The liquid flow accelerates from a subcritical with relatively high conductivity. On the other hand, it
[84]
to a supercritical regime at a critical point near the exit is not always attainable before the mode obtained in
of feeding needle by considering self-induction effects experiments when the values of working parameters are
and jets issued from Taylor cone are always supercritical given.
at region before breakup point . A point of instability This paper reviews the initiation condition of cone-jet.
[67]
is defined as a boundary line to separate the supercritical The critical voltage predicted by Taylor does not account
region and the breakup regions and supercritical region for EHD effect caused by subsequent jet emission, and
prevents upstream propagation of disturbance as long the semi-vertical angle is not always Taylor angle. The
as the point of instability is far away from the critical following section study effects of processing parameters
point . Transition between jetting and dripping is related and materials properties on the operating diagram of cone-
[67]
to transition between convective and absolute instability jet. Domain of cone-jet may become different by small
transitions . Convective instability is defined as the changes in the selection of parameters. The minimum
[85]
surface energy that is sufficiently smaller than the kinetic flow rate in operating diagram is not, simply, the flow rate
energy per unit jet length, and the disturbance can only due to the upstream pressure, but rather the specific flow
propagate and increase downstream . The disturbance rate that causes electrical stress to strip off (or shear) the
[85]
can propagate and increase both upstream and downstream surface charge layer of the fluid. Several scaling laws have
for absolute instability. The critical convective velocity been proposed to predict jet diameter and emitted current,
in the developed jet that relates to critical Weber number and each of them is applied to different parametric ranges
mainly depends on the viscosity of fluid that scale as according to material attribute and working condition.
the Reynolds number during the transition between Communities have not reached an agreement on the
the absolute and convective instability. Herrera et al. charge transport mechanism. In the future, it is helpful
introduced different electric parameters (relaxation to study what the predominant transport mechanism is,
parameter α, liquid relative permittivity β, and electric especially near the nozzle. It is difficult to measure a thin
bond number χ) to the classical Leib and Goldstein curve free jet whose diameter is usually at the verge of optical
International Journal of Bioprinting (2019)–Volume 5, Issue 1 15