Page 48 - IJB-5-2
P. 48
Multicomponent bioprinting based on microfluidic printheads
A C D
E F
B
G H
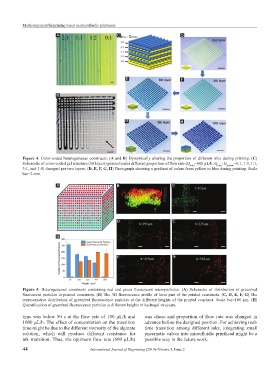
Figure 4. Color-coded heterogeneous constructs. (A and B) Dynamically altering the proportion of different inks during printing. (C)
Schematic of color-coded gel structure (10 layers) printed under different proportion of flow rate (Q total =600 µL/h, Q blue : Q yellow =0:1, 1:3, 1:1,
3:1, and 1:0) changed per two layers. (D, E, F, G, H) Photograph showing a gradient of colors from yellow to blue during printing. Scale
bar=2 mm.
A B C
D E
H
F G
Figure 5. Heterogeneous constructs containing red and green fluorescent microparticles. (A) Schematic of distribution of green/red
fluorescent particles in printed constructs. (B) The 3D fluorescence profile of local part of the printed constructs. (C, D, E, F, G) The
representative distribution of green/red fluorescence particles at the different heights of the printed construct. Scale bar=100 µm. (H)
Quantification of green/red fluorescence particles at different heights in hydrogel structure.
time was below 50 s at the flow rate of 100 µL/h and was chose and proportion of flow rate was changed in
1000 µL/h. The effect of concentration on the transition advance before the designed position. For achieving real-
time might be due to the different viscosity of the alginate time transition among different inks, integrating small
solution, which will produce different resistance for pneumatic valves into microfluidic printhead might be a
ink transition. Thus, the optimum flow rate (600 µL/h) possible way in the future work.
44 International Journal of Bioprinting (2019)–Volume 5, Issue 2