Page 231 - IJB-10-5
P. 231
International Journal of Bioprinting Effect of ingredient flow speed
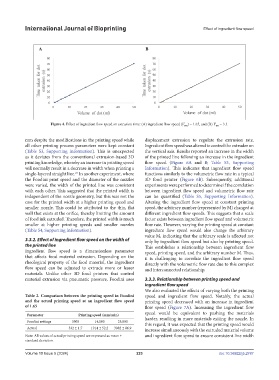
Figure 4. Effect of ingredient flow speed on extrusion time: (A) ingredient flow speed (V ) = 1.65, and (B) V = 3.3.
IFS IFS
mm despite the modifications in the printing speed while displacement extrusion to regulate the extrusion rate.
all other printing process parameters were kept constant Ingredient flow speed was altered to control the extruder on
(Table S3, Supporting Information). This is unexpected the vertical axis. Results reported an increase in the width
as it deviates from the conventional extrusion-based 3D of the printed line following an increase in the ingredient
printing knowledge, whereby an increase in printing speed flow speed (Figure 6A and B; Table S3, Supporting
will normally result in a decrease in width when printing a Information). This indicates that ingredient flow speed
single-layered straight line. In another experiment, where functions similarly to the volumetric flow rate in a typical
23
the Foodini print speed and the diameter of the nozzles 3D food printer (Figure 6B). Subsequently, additional
were varied, the width of the printed line was consistent experiments were performed to determine if the correlation
with each other. This suggested that the printed width is between ingredient flow speed and volumetric flow rate
independent of the nozzle geometry, but this was not the can be quantified (Table S5, Supporting Information).
case for the printed width at a higher printing speed and Altering the ingredient flow speed at constant printing
smaller nozzle. This could be attributed to the thin, flat speed, the arbitrary number (represented by M) changed at
wall that exists at the orifice, thereby limiting the amount different ingredient flow speeds. This suggests that a scale
of food ink extruded. Therefore, the printed width is much factor exists between ingredient flow speed and volumetric
smaller at higher printing speeds and smaller nozzles flow rate. However, varying the printing speed at constant
(Table S4, Supporting Information). ingredient flow speed would also change the arbitrary
value M, indicating that the arbitrary scale is affected not
3.3.2. Effect of ingredient flow speed on the width of only by ingredient flow speed but also by printing speed.
the printed line This establishes a relationship between ingredient flow
Ingredient flow speed is a dimensionless parameter speed, printing speed, and the arbitrary number M. Thus,
that affects food material extrusion. Depending on the it is challenging to correlate the ingredient flow speed
rheological property of the food material, the ingredient directly with the volumetric flow rate due to this complex
flow speed can be adjusted to extrude more or lesser and interconnected relationship.
materials. Unlike other 3D food printers that control
material extrusion via pneumatic pressure, Foodini uses 3.3.3. Relationship between printing speed and
ingredient flow speed
We also evaluated the effects of varying both the printing
Table 2. Comparison between the printing speed in Foodini speed and ingredient flow speed. Notably, the actual
and the actual printing speed at an ingredient flow speed printing speed decreased with an increase in ingredient
of 1.65 flow speed (Figure 7A). Increasing the ingredient flow
Parameter Printing speed (mm/min) speed would be equivalent to pushing the materials
Foodini settings 3500 14,000 25,000 harder, resulting in more materials exiting the nozzle. In
this regard, it was expected that the printing speed would
Actual 532 ± 1.7 1914 ± 52.2 3082 ± 86.9 increase simultaneously with the extruded material volume
Note: All values of actual printing speed are expressed as mean ± and ingredient flow speed to ensure consistent line width
standard deviation.
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 223 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2787