Page 363 - IJB-10-5
P. 363
International Journal of Bioprinting Printing organoids in peptide matrices
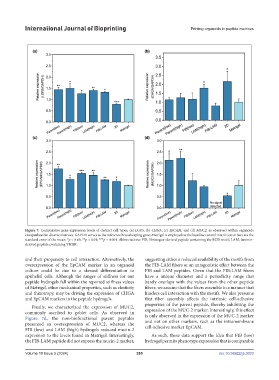
Figure 7. Comparative gene expression levels of distinct cell types, (a) LGR5, (b) CHGA, (c) EpCAM, and (d) MUC2, as observed within organoids
encapsulated in diverse matrices. GAPDH serves as the reference housekeeping gene; Matrigel is employed as the baseline control matrix; error bars are the
standard error of the mean; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Abbreviations: FIB, fibrinogen-derived peptide containing the RGD motif; LAM, laminin-
derived peptide containing YIGSR.
and their propensity to cell interaction. Alternatively, the suggesting either a reduced availability of the motifs from
overexpression of the EpCAM marker in an organoid the FIB-LAM fibers or an antagonistic effect between the
culture could be due to a skewed differentiation to FIB and LAM peptides. Given that the FIB-LAM fibers
epithelial cells. Although the ranges of stiffness for our have a unique diameter and a periodicity range that
peptide hydrogels fall within the reported stiffness values barely overlaps with the values from the other peptide
of Matrigel, other mechanical properties, such as elasticity fibers, we assume that the fibers assemble in a manner that
and thixotropy, may be driving the expression of CHGA hinders cell interaction with the motifs. We also presume
and EpCAM markers in the peptide hydrogels. that fiber assembly affects the intrinsic cell-adhesive
properties of the parent peptide, thereby inhibiting the
Finally, we characterized the expression of MUC2,
commonly ascribed to goblet cells. As observed in expression of the MUC-2 marker. Interestingly, this effect
is only observed in the expression of the MUC-2 marker
Figure 7d, the non-biofunctional parent peptides and not on other markers, such as the intramembrane
presented an overexpression of MUC2, whereas the cell-adhesive marker EpCAM.
FIB (low) and LAM (high) hydrogels reduced mucin-2
expression to the levels found in Matrigel. Interestingly, As such, these data support the idea that FIB (low)
the FIB-LAM peptide did not express the mucin-2 marker, hydrogel permits phenotype expression that is comparable
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 355 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3033