Page 365 - IJB-10-5
P. 365
International Journal of Bioprinting Printing organoids in peptide matrices
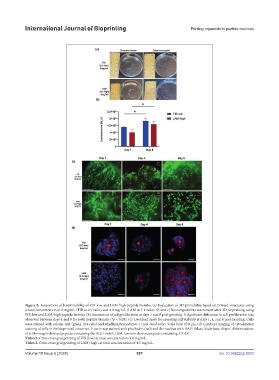
Figure 8. Assessment of bioprintability of FIB-low and LAM-high peptide bioinks. (a) Evaluation of 3D printability based on printed structures using
a total concentration of 6 mg/mL (FIB at 2:1 ratio) and 4.0 mg/mL (LAM at 1:1 ratio). (b and c) Biocompatibility assessment after 3D bioprinting using
FIB-low and LAM-high peptide bioinks. (b) Assessment of cell proliferation at days 1 and 8 post-printing. A significant difference in cell proliferation was
observed between days 1 and 8 for both peptide bioinks (*p < 0.05). (c) Live/dead assay for assessing cell viability at days 1, 4, and 8 post-printing. Cells
were stained with calcein-AM (green, live cells) and ethidium homodimer-1 (red, dead cells). Scale bars: 650 µm. (d) Confocal imaging of cytoskeleton
staining of cells in the bioprinted construct. F-actin was stained with phalloidin (red) and the nucleus with DAPI (blue). Scale bars: 40 µm. Abbreviations:
FIB, fibrinogen-derived peptide containing the RGD motif; LAM, laminin-derived peptide containing YIGSR.
Video 1. Criss-cross grid printing of FIB (low) at total concentration of 6 mg/mL.
Video 2. Criss-cross grid printing of LAM (high) at total concentration of 4.5 mg/mL.
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 357 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3033