Page 459 - IJB-10-5
P. 459
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed plasma devices for decontamination
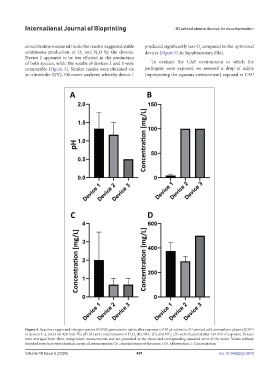
concentration measured inside the reactor suggested stable produced significantly less O compared to the optimized
3
continuous production of O and N O by the devices. devices (Figure S2 in Supplementary File).
3
2
Device 1 appeared to be less efficient in the production
of both species, while the results of devices 2 and 3 were To evaluate the CAP environment to which the
comparable (Figure 3). Similar results were obtained via pathogens were exposed, we assessed a drop of saline
an ultraviolet (UV)-100 ozone analyzer, whereby device 1 (representing the aqueous environment) exposed to CAP
Figure 4. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) generated in saline after exposure (of 30 µL saline) to 3D-printed cold atmospheric plasma (CAP)
-
in devices 1, 2, and 3 for 120 min. The pH (A) and concentrations of H O (B), NO (C), and NO (D) were measured after 120 min of exposure. Results
-
2
2
3
2
were averaged from three independent measurements and are presented as the mean and corresponding standard error of the mean. Values without
depicted error bars were identical across all measurements (i.e., standard error of the mean = 0). Abbreviation: c: Concentration.
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 451 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3679