Page 462 - IJB-10-5
P. 462
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed plasma devices for decontamination
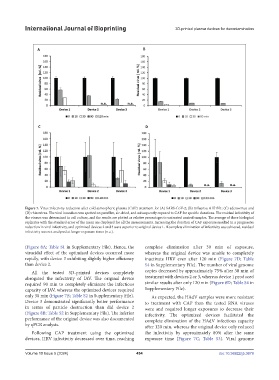
Figure 7. Virus infectivity reduction after cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) treatment for (A) SARS-CoV-2; (B) influenza A H1N1; (C) adenovirus; and
(D) rhinovirus. The viral inoculum was spotted on parafilm, air-dried, and subsequently exposed to CAP for specific durations. The residual infectivity of
the viruses was determined in cell culture, and the results are plotted as relative percentages to untreated control samples. The average of three biological
replicates with the standard error of the mean are displayed for all the measurements. Increasing the duration of CAP exposure resulted in a progressive
reduction in viral infectivity, and optimized devices 2 and 3 were superior to original device 1. If complete elimination of infectivity was achieved, residual
infectivity was not analyzed at longer exposure times (n.a.).
(Figure 8A; Table S1 in Supplementary File). Hence, the complete elimination after 30 min of exposure,
virucidal effect of the optimized devices occurred more whereas the original device was unable to completely
rapidly, with device 3 exhibiting slightly higher efficiency inactivate HRV even after 120 min (Figure 7D; Table
than device 2. S4 in Supplementary File). The number of viral genome
All the tested 3D-printed devices completely copies decreased by approximately 75% after 30 min of
abrogated the infectivity of IAV. The original device treatment with devices 2 or 3, whereas device 1 produced
required 90 min to completely eliminate the infectious similar results after only 120 min (Figure 8D; Table S4 in
capacity of IAV, whereas the optimized devices required Supplementary File).
only 30 min (Figure 7B; Table S2 in Supplementary File). As expected, the HAdV samples were more resistant
Device 3 demonstrated significantly better performance to treatment with CAP than the tested RNA viruses
in terms of particle destruction than did device 2 were and required longer exposures to decrease their
(Figure 8B; Table S2 in Supplementary File). The inferior infectivity. The optimized devices facilitated the
performance of the original device was also documented complete elimination of the HAdV infectious capacity
by qPCR analysis. after 120 min, whereas the original device only reduced
Following CAP treatment using the optimized the infectivity by approximately 80% after the same
devices, HRV infectivity decreased over time, reaching exposure time (Figure 7C; Table S3). Viral genome
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 454 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3679