Page 541 - IJB-10-5
P. 541
International Journal of Bioprinting Biomimetic scaffolds for mandibular repair
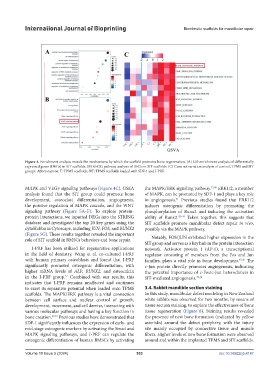
Figure 4. Enrichment analysis reveals the mechanisms by which the scaffold promotes bone regeneration. (A) GO enrichment analysis of differentially
expressed genes (DEGs) in SIT scaffolds. (B) KEGG pathway analysis of DEGs in SIT scaffolds. (C) Gene set variation analysis of control, TPMS and SIT
groups. Abbreviations: T: TPMS scaffolds; SIT: TPMS scaffolds loaded with SDF-1 and I-PRF.
MAPK and VEGF signaling pathways (Figure 4C). GSEA the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. 37,40 ERK1/2, a member
analysis found that the SIT group could promote bone of MAPK, can be promoted by SDF-1 and plays a key role
development, osteoclast differentiation, angiogenesis, in angiogenesis. Previous studies found that ERK1/2
41
the positive regulation of MAPK cascade, and the WNT induces osteogenic differentiation by promoting the
signaling pathway (Figure 5A–F). To explore protein- phosphorylation of Runx2 and inducing the activation
protein interactions, we inputted DEGs into the STRING ability of Runx2. 42–44 Taken together, this suggests that
database and investigated the top 20 key genes using the SIT scaffolds promote mandibular defect repair in vivo,
cytoHubba in Cytoscape, including JUN, FOS, and RUNX2 possibly via the MAPK pathway.
(Figure 5G). These results together revealed the important
role of SIT scaffold in BMSCs behaviors and bone repair. Notably, FOS/JUN exhibited higher expression in the
SIT group and serves as a key hub in the protein interaction
I-PRF has been utilized for regenerative applications network. Activator protein 1 (AP-1), a transcriptional
in the field of dentistry. Wang et al. co-cultured I-PRF regulator consisting of members from the Fos and Jun
with human primary osteoblasts and found that I-PRF families, plays a vital role in bone development. 45,46 The
significantly promoted osteogenic differentiation, with c-Jun protein directly promotes angiogenesis, indicating
higher mRNA levels of ALP, RUNX2, and osteocalcin the potential importance of c-Fos/c-Jun heterodimers in
in the I-PRF group. Combined with our results, this SIT-mediated angiogenesis. 47,48
37
indicates that I-PRF remains unaffected and continues
to exert its reparative potential when loaded onto TPMS 3.4. Rabbit mandible section staining
scaffolds. The MAPK/ERK pathway is a vital connection In this study, mandibular defect modeling in New Zealand
between cell surface and nuclear control of growth, white rabbits was observed for two months, by means of
development, movement, and cell demise, interacting with tissue section staining, to explore the effectiveness of bone
various molecular pathways and having a key function in tissue regeneration (Figure 6). Staining results revealed
bone creation. 38,39 Previous studies have demonstrated that the presence of new bone formation (indicated by yellow
SDF-1 significantly influences the expression of early- and asterisks) around the defect periphery, with the injury
mid-stage osteogenic markers by activating the Smad and site mainly occupied by connective tissue and muscle
MAPK signaling pathways, and I-PRF can regulate the fibers. Higher levels of new bone formation were observed
osteogenic differentiation of human BMSCs by activating around and within the implanted TPMS and SIT scaffolds.
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 533 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4147