Page 33 - IJB-6-1
P. 33
Zhang, et al.
cells to create tissue scaffolds for heart valve 2 SBE 3D printing types in TE
tissue [11,12] , bone tissue [13,14] , cartilage tissue [15] ,
blood vessel [16] , and skin tissue [17] . Recently, a The SBE 3D printing technique involves extruding
concept study has described building a scaffold a continuous filament of ink containing biomaterials
with simultaneous control over multiple with or without cells through a nozzle to form 3D
biomaterial inks in the desired combination to woodpile structures in a layer-by-layer manner.
create biomimetic and functional scaffolds that The SBE 3D printer includes a three-axis position
closely mimic natural tissue [18] . Despite these system, print head, and print platform. The print
advances, the lack of feasible inks, particularly head is moved to appropriate locations on the build
bio-composite ink, prevents the clinical use of platform by the three-axis position system; inks
current SBE 3D printed scaffolds. Scaffolds are extruded from the syringe on the print head
with appropriate levels of filament uniformity in the X, Y, and Z directions [9,10,20] . The printed
cannot easily be obtained; in addition, there is filament resolution is dependent on the print head
a poor fidelity between the structures of printed nozzle diameter, which can be varied in the range
scaffolds and the computer models of these of 10–1000 µm. As shown in Figure 1A-C, SBE
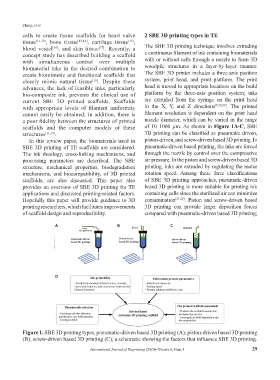
structures [11,19] . 3D printing can be classified as pneumatic driven,
In this review paper, the biomaterials used in piston-driven, and screw-driven based 3D printing. In
SBE 3D printing of TE scaffolds are considered. pneumatic-driven based printing, the inks are forced
The ink rheology, cross-linking mechanisms, and through the nozzle by control over the compressive
processing parameters are described. The SBE air pressure. In the piston and screw-driven based 3D
structure, mechanical properties, biodegradation printing, inks are extruded by regulating the motor
mechanisms, and biocompatibility, of 3D printed rotation speed. Among these three classifications
scaffolds, are also discussed. This paper also of SBE 3D printing approaches, pneumatic-driven
provides an overview of SBE 3D printing for TE based 3D printing is more suitable for printing ink
applications and discussed printing-related factors. containing cells since the sterilized air can minimize
Hopefully this paper will provide guidance to 3D contamination [21,22] . Piston and screw-driven based
printing researchers, which facilitates improvements 3D printing can provide larger deposition forces
of scaffold design and reproducibility. compared with pneumatic-driven based 3D printing;
A B C
D
Figure 1. SBE 3D printing types, pneumatic-driven based 3D printing (A); piston-driven based 3D printing
(B); screw-driven based 3D printing (C); a schematic showing the factors that influence SBE 3D printing.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 1 29