Page 37 - IJB-6-1
P. 37
Zhang, et al.
carbon nanotubes (CNT). The CNT improved the ink was higher than those of inks containing three
mechanical behavior of the scaffolds. The in vitro types of cells. As the cell density in the alginate
results showed that HA improved bioactivity; inks is increased, a reduction in viscosity can be
good cell adhesion and spreading were noted on obtained. The results suggest that cells containing
the scaffold surface. Although the use of SBE 3D cytoplasm can be treated as a fluid with low
printing to create polymer/ceramic composites is viscosity; as such, the interactions among cells
promising for TE applications, only a few studies likely act as lubricants and reduce the viscosity .
[38]
to this point have investigated the ink printability Dávila and d’Ávila formulated laponite/alginate
[39]
and processing parameters. Additional studies inks without cells and analyzed the ink rheology in
should be performed to understand optimization terms of viscosity, viscoelasticity behavior, and ink
of the ink rheology, processing parameters, and recovery behavior. As the laponite concentration
cross-linking mechanisms for fabrication of SBE increased from 0 to 6 wt%, an increase in viscosity
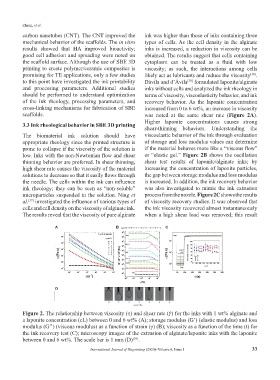
scaffolds. was noted at the same shear rate (Figure 2A).
Higher laponite concentrations causes strong
3.3 Ink rheological behavior in SBE 3D printing
shear-thinning behaviors. Understanding the
The biomaterial ink solution should have viscoelastic behavior of the ink through evaluation
appropriate rheology since the printed structure is of storage and loss modulus values can determine
prone to collapse if the viscosity of the solution is if the material behaves more like a “viscous flow”
low. Inks with the non-Newtonian flow and shear or “elastic gel.” Figure 2B shows the oscillation
thinning behavior are preferred. In shear thinning, shear test results of laponite/alginate inks; by
high shear rate causes the viscosity of the material increasing the concentration of laponite particles,
solutions to decrease so that it easily flows through the gap between storage modulus and loss modulus
the needle. The cells within the ink can influence is increased. In addition, the ink recovery behavior
ink rheology; they can be seen as “non-soluble” was also investigated to mimic the ink extrusion
microparticles suspended in the solution. Ning et process from the nozzle. Figure 2C shows the results
al. investigated the influence of various types of of viscosity recovery studies. It was observed that
[37]
cells and cell density on the viscosity of alginate ink. the ink viscosity recovered almost instantaneously
The results reveal that the viscosity of pure alginate when a high shear load was removed; this result
A B C
D
Figure 2. The relationship between viscosity (η) and shear rate ( γ ) for the inks with 1 wt% alginate and
a laponite concentration (cL) between 0 and 6 wt% (A); storage modulus (G’) (elastic modulus) and loss
modulus (G’’) (viscous modulus) as a function of strain (γ) (B); viscosity as a function of the time (t) for
the ink recovery test (C); microscopy images of the extrusion of alginate/laponite inks with the laponite
between 0 and 6 wt%. The scale bar is 1 mm (D) .
[39]
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 1 33