Page 111 - IJB-6-2
P. 111
Owen, et al.
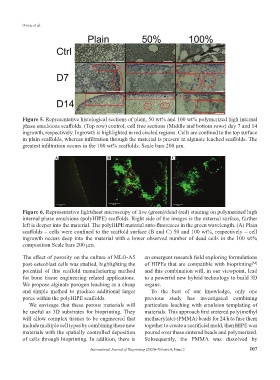
Figure 5. Representative histological sections of plain, 50 wt% and 100 wt% polymerized high internal
phase emulsions scaffolds. (Top row) control, cell free sections (Middle and bottom rows) day 7 and 14
ingrowth, respectively. Ingrowth is highlighted in red circled regions. Cells are confined to the top surface
in plain scaffolds, whereas infiltration through the material is present in alginate leached scaffolds. The
greatest infiltration occurs in the 100 wt% scaffolds. Scale bars 200 µm.
A B C
Figure 6. Representative lightsheet microscopy of live (green)/dead (red) staining on polymerized high
internal phase emulsions (polyHIPE) scaffolds. Right side of the images is the external surface, further
left is deeper into the material. The polyHIPE material auto-fluoresces in the green wavelength. (A) Plain
scaffolds – cells were confined to the scaffold surface (B and C) 50 and 100 wt%, respectively – cell
ingrowth occurs deep into the material with a lower observed number of dead cells in the 100 wt%
composition Scale bars 200 μm.
The effect of porosity on the culture of MLO-A5 an emergent research field exploring formulations
post-osteoblast cells was studied, highlighting the of HIPEs that are compatible with bioprinting
[34]
potential of this scaffold manufacturing method and this combination will, in our viewpoint, lead
for bone tissue engineering related applications. to a powerful new hybrid technology to build 3D
We propose alginate porogen leaching as a cheap organs.
and simple method to produce additional larger To the best of our knowledge, only one
pores within the polyHIPE scaffolds. previous study has investigated combining
We envisage that these porous materials will particulate leaching with emulsion templating of
be useful as 3D substrates for bioprinting. They materials. This approach first sintered poly(methyl
will allow complex tissues to be engineered that methacrylate) (PMMA) beads for 24 h to fuse them
include multiple cell types by combining these new together to create a sacrificial mold, then HIPE was
materials with the spatially controlled deposition poured over these sintered beads and polymerized.
of cells through bioprinting. In addition, there is Subsequently, the PMMA was dissolved by
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 2 107