Page 212 - IJB-10-6
P. 212
International Journal of Bioprinting Effect of G/GO on photocurable resin structure
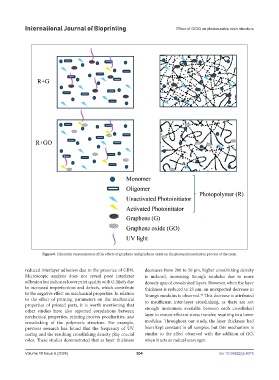
Figure 6. Schematic representation of the effects of graphene and graphene oxide on the photopolymerization process of the resin.
reduced interlayer adhesion due to the presence of GBN. decreases from 200 to 50 μm, higher crosslinking density
Microscopic analysis does not reveal poor interlayer is induced, increasing Young’s modulus due to more
adhesion but indicates lower print quality with G, likely due densely spaced crosslinked layers. However, when the layer
to increased imperfections and defects, which contribute thickness is reduced to 25 μm, an unexpected decrease in
to the negative effect on mechanical properties. In relation Young’s modulus is observed. This decrease is attributed
48
to the effect of printing parameters on the mechanical to insufficient inter-layer crosslinking, as there are not
properties of printed parts, it is worth mentioning that enough monomers available between each crosslinked
other studies have also reported correlations between
mechanical properties, printing process peculiarities, and layer to ensure efficient stress transfer, resulting in a lower
crosslinking of the polymeric structure. For example, modulus. Throughout our study, the layer thickness had
previous research has found that the frequency of UV been kept constant in all samples, but this mechanism is
curing and the resulting crosslinking density play crucial similar to the effect observed with the addition of GO,
roles. These studies demonstrated that as layer thickness when it acts as radical scavenger.
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 204 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4075