Page 134 - IJB-7-3
P. 134
Multiresponsive Graphene-Oxide Embedded ECM Hydrogel for 3D Bioprinting
are limited by their spatial distribution within the where L is the thickness of the rGO sheet, A is
hydrogel. Therefore, considering that the hydrogel the contact area of the sheet with the probes, and R is
alone is not electroconductive, when a current is the previously calculated resistance of the sheet. This
applied, it will only flow through interconnected procedure was also performed for a GO sheet to estimate
networks at the microscale. However, such networks the possible effects of ascorbic acid and temperature
might not necessarily be all well connected. Since treatment on the electroconductivity.
electric currents would be difficult to measure under
the conditions of this scenario and present high 2.16. Statistical analysis
variability, electroconductivity of the GO reduced All experiments were performed in triplicate, unless
in situ was measured by creating a densely packed
rGO’s squared sheet of 1 cm . For this, GO dispersed otherwise stated and quantitative data are expressed
2
in DMEM culture medium supplemented with 0.5 mM as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis
ascorbic acid was incubated at 37°C for 3 days and was performed with Student t-tests and P < 0.05 was
subsequently centrifuged at 5000 rpm. The resulting considered as statistically significant.
pellet was lyophilized for 24 h and the obtained dry 3. Results and discussion
powder was resuspended in 96% (v/v) ethanol at a high
concentration of 20 mg/mL to finally deposit it over a 3.1. Preparation and functionalization of
squared 1 cm glass slide. To favor sheet formation by decellularized small intestine submucosa
2
ethanol evaporation, the preparation was left overnight
at room temperature. Then, variable currents (Keithley hydrogels
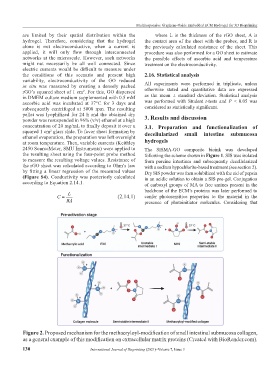
2450 SourceMeter, SMU Instruments) were applied to The SISMA-GO composite bioink was developed
the resulting sheet using the four-point probe method following the scheme shown in Figure 1. SIS was isolated
to measure the resulting voltage values. Resistance of from porcine intestines and subsequently decellularized
the rGO sheet was calculated according to Ohm’s law with a sodium hypochlorite-based treatment (see section 2).
by fitting a linear regression of the measured values Dry SIS powder was then solubilized with the aid of pepsin
(Figure S4). Conductivity was posteriorly calculated in an acidic solution to obtain a SIS pre-gel. Conjugation
according to Equation 2.14.1. of carboxyl groups of MA to free amines present in the
backbone of the ECM’s proteins was later performed to
L
C = (2.14.1) confer photosensitive properties to the material in the
RA presence of photoinitiator molecules. Considering that
Figure 2. Proposed mechanism for the methacryloyl-modification of small intestinal submucosa collagen,
as a general example of this modification on extracellular matrix proteins (Created with BioRender.com).
130 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3