Page 135 - IJB-7-3
P. 135
Rueda-Gensini, et al.
collagen is the main structural component of dECMs, the with serum proteins and Tris-HCl buffer was added during
proposed mechanism for EDC/NHS mediated conjugation the resuspension procedure to raise the pH of the hydrogel
of MA to collagen backbones is shown in Figure 2, where to 7 and to adjust the ionic balance for posterior cell
EDC and NHS are zero-length crosslinkers that activate incorporation.
the nucleophilic reaction but are not included in the
conjugation . This is convenient since this biochemical 3.2. GO synthesis and dispersion in SISMA
[48]
modification involves no bulky elements that significantly hydrogels
modify the native dECM composition and, before cell GO nanosheets were successfully synthesized upon
embedding, the reaction by-products are eliminated with graphite exfoliation and oxidation procedures. However,
the aid of dialysis. ECM free amines were previously the colloidal stability of GO in SISMA hydrogels was
quantified with the TNBSA assay to determine the a special concern since previous studies have reported
necessary reagent concentrations. An efficient biochemical that GO forms aggregates in acidic media and biological
conjugation reaction was demonstrated by an 81.5 ± buffers , two of the essential media for SISMA hydrogel
[53]
0.8% reduction in free-amine content after methacryloyl preparation. The electrostatic repulsion between GO
conjugation to SIS pre-gels (i.e., SISMA) (Figure S5). nanosheets has shown to be the main driving force for their
This strongly suggests a high degree of functionalization colloidal stability , and this phenomenon is impaired
[45]
when compared with previously reported values of other at low pH due to the protonation of GO’s carboxylic
functionalization methods with MA [43,49,50] , which ranged groups. Similarly, the sp -hybridized carbon backbone of
2
between 20% and 30%. Furthermore, it was comparable GO has a high degree of surface planarity that facilitates
to other methods based on methacrylic anhydride, which electrostatic surface charging in the presence of electrolyte
reported values between 71% and 87% [13,51,52] . Dialyzed solutions, resulting in irreversible sheet aggregation .
[54]
SISMA samples were then lyophilized and resolubilized to Accordingly, we hypothesized that by coating GO surface
incorporate the GO nanosheets and the photoinitiator (i.e., with hydrophilic serum proteins from culture media,
RF). Moreover, a pH 8.5 DMEM solution supplemented GO aggregation could be largely avoided. This would
A B
C D
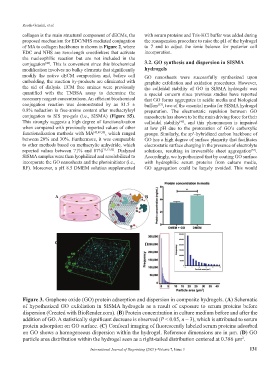
Figure 3. Graphene oxide (GO) protein adsorption and dispersion in composite hydrogels. (A) Schematic
of hypothesized GO exfoliation in SISMA hydrogels as a result of exposure to serum proteins before
dispersion (Created with BioRender.com). (B) Protein concentration in culture medium before and after the
addition of GO. A statistically significant decrease is observed (P < 0.05, n = 3), which is attributed to serum
protein adsorption on GO surface. (C) Confocal imaging of fluorescently labeled serum proteins adsorbed
on GO shows a homogeneous dispersion within the hydrogel. Reference dimensions are in µm. (D) GO
particle area distribution within the hydrogel seen as a right-tailed distribution centered at 0.386 µm .
2
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3 131