Page 25 - IJB-7-3
P. 25
Ren, et al
of to its and
cross-linking bioink using light and layer- solidification light initiator can damage cells
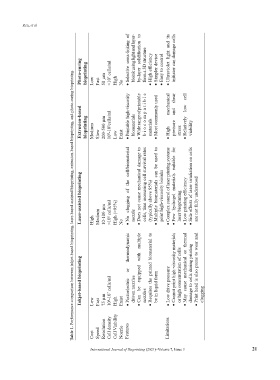
Photo‑curing bioprinting Low Fast 50 µm >10 7 cells/ml High No Selective • by-layer form a 3D structure • High efficiency • Simpler device • Easy to control Ultraviolet • cell
Table 1. Performance comparison between inkjet-based bioprinting, laser-based assisted bioprinting, extrusion-based bioprinting, and photo-curing bioprinting.
Extrusion‑based bioprinting Medium Slow 200-500 µm 10 8 -10 9 cells/ml Low Exist Printable high-viscosity • biomaterials Wide range of printable • biocompatible materials • Most commonly used mechanical High • shear pressure and stress low Relatively • viability
cell/biomaterial to used be can for suitable
Laser‑assisted bioprinting High Medium 10-100 µm >10 8 cells/ml High (>95%) No the of clogging No • nozzle Does not cause mechanical damage to • cells, thus increasing cell survival rates (typically above 95%) biomaterials Multiple • print high-viscosity bioinks Complex control of laser printing systems • materials hydrogel Few • laser bioprinting • Low printing efficiency Side effects of la
thermodynamic multiple with to biomaterial thermal or
Inkjet‑based bioprinting Low Fast 75 µm 10 6 -10 7 cells/ml High Exist or Piezoelectric • driven nozzles equipped be Can • nozzles printed the Requires • be in liquid form • Low drive pressure Cannot print high-viscosity materials • or high concentration of cells mechanical cause May • damage to cells during printing Print head is also prone to wear and • clogging
Cost Speed Resolution Cell density Cell Viability Nozzle Features Limitations
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3 21