Page 43 - IJB-7-3
P. 43
Mei, et al.
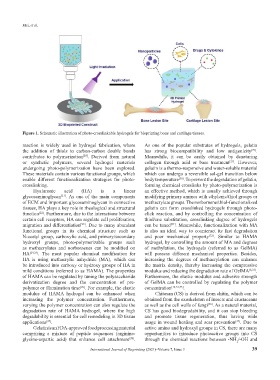
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of photo-crosslinkable hydrogels for bioprinting bone and cartilage tissues.
reaction is widely used in hydrogel fabrication, where As one of the popular substrates of hydrogels, gelatin
the addition of thiols to carbon-carbon double bonds has strong biocompatibility and low antigenicity .
[29]
contributes to polymerization . Derived from natural Meanwhile, it can be easily obtained by denaturing
[20]
or synthetic polymers, several hydrogel materials collagen through acid or base treatment . However,
[21]
undergoing photo-polymerization have been explored. gelatin is a thermo-responsive and water-soluble material
These materials contain various functional groups, which which can undergo a reversible sol-gel transition below
enable different functionalization strategies for photo- body temperature . To prevent the degradation of gelatin,
[30]
crosslinking. forming chemical crosslinks by photo-polymerization is
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a linear an effective method, which is usually achieved through
glycosaminoglycan . As one of the main components modifying primary amines with ethylenic/thiol groups or
[21]
of ECM and important glycosaminoglycan in connective methacrylate groups. The norbornene/thiol-functionalized
tissues, HA plays a key role in rheological and structural gelatin can form crosslinked hydrogels through photo-
function . Furthermore, due to the interactions between click reaction, and by controlling the concentration of
[22]
certain cell receptors, HA can regulate cell proliferation, thiol/ene substitution, crosslinking degree of hydrogels
migration and differentiation . Due to many abundant can be tuned . Meanwhile, functionalization with MA
[23]
[31]
functional groups in its chemical structure such as is also an ideal way to counteract its fast degradation
N-acetyl group, carboxylic acid, and primary/secondary and poor mechanical property . Similar to HAMA
[32]
hydroxyl groups, photo-polymerizable groups such hydrogel, by controlling the amount of MA and degrees
as methacrylates and norbornenes can be modified on of methylation, the hydrogels (referred to as GelMA)
HA [24,25] . The most popular chemical modification for will possess different mechanical properties. Besides,
HA is using methacrylic anhydride (MA), which can increasing the degrees of methacrylation can enhance
be introduced into carboxy or hydroxy groups of HA in the matrix density, thereby increasing the compressive
mild conditions (referred to as HAMA). The properties modulus and reducing the degradation rate of GelMA [6,33] .
of HAMA can be regulated by tuning the polysaccharide Furthermore, the elastic modulus and adhesive strength
derivatization degree and the concentration of pre- of GelMA can be controlled by regulating the polymer
polymer or illumination time . For example, the elastic concentration [12,34,35] .
[26]
modulus of HAMA hydrogel can be enhanced when Chitosan (CS) is derived from chitin, which can be
increasing the polymer concentration. Furthermore, obtained from the exoskeleton of insects and crustaceans
varying the polymer concentration can also regulate the as well as the cell walls of fungi . As a natural material,
[36]
degradation rate of HAMA hydrogel, where the high CS has good biodegradability, and it can stop bleeding
degradability is essential for cell remodeling in 3D tissue and promote tissue regeneration, thus having wide
applications . usage in wound healing and scar prevention . Due to
[27]
[37]
Gelatin is an FDA-approved food processing material active amino and hydroxyl groups in CS, there are many
comprising a mixture of peptide sequences (arginine- opportunities to introduce photoactive groups into CS
glycine-aspartic acid) that enhance cell attachment . through the chemical reactions between -NH /-OH and
[28]
2
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3 39