Page 60 - IJB-7-3
P. 60
Heart-on-a-chip
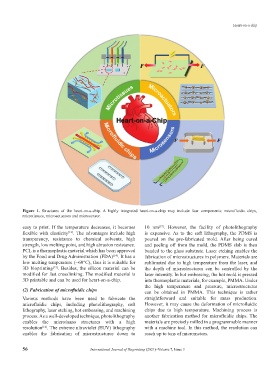
Figure 1. Structures of the heart-on-a-chip. A highly integrated heart-on-a-chip may include four components: microfluidic chips,
microtissues, microactuators and microsensor.
easy to print. If the temperature decreases, it becomes 10 nm . However, the facility of photolithography
[17]
flexible with elasticity . The advantages include high is expensive. As to the soft lithography, the PDMS is
[12]
transparency, resistance to chemical solvents, high poured on the pre-fabricated mold. After being cured
strength, low melting point, and high abrasion resistance. and peeling off from the mold, the PDMS slab is then
PCL is a thermoplastic material which has been approved bonded to the glass substrate. Laser etching enables the
by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) . It has a fabrication of microstructures in polymers. Materials are
[14]
low melting temperature (~60°C), thus it is suitable for sublimated due to high temperature from the laser, and
3D bioprinting . Besides, the silicon material can be the depth of microstructures can be controlled by the
[13]
modified for fast crosslinking. The modified material is laser intensity. In hot embossing, the hot mold is pressed
3D printable and can be used for heart-on-a-chip. into thermoplastic materials, for example, PMMA. Under
the high temperature and pressure, microstructures
(2) Fabrication of microfluidic chips can be obtained in PMMA. This technique is rather
Various methods have been used to fabricate the straightforward and suitable for mass production.
microfluidic chips, including photolithography, soft However, it may cause the deformation of microfluidic
lithography, laser etching, hot embossing, and machining chips due to high temperature. Machining process is
process. As a well-developed technique, photolithography another fabrication method for microfluidic chips. The
enables the micro/nano structures with a high materials are precisely milled in a programmable manner
resolution . The extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography with a machine tool. In this method, the resolution can
[16]
enables the fabrication of microstructures down to reach up to tens of micrometers.
56 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3